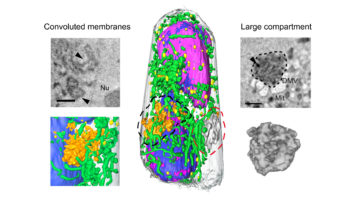
In this work, researchers illustrated the potential of soft x-ray tomography to rapidly characterize and quantify the structural changes induced in cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, revealing profound alterations of the subcellular architecture induced by viral infection over time. Read more »
Improving the Efficiency of Atmospheric Water Harvesting
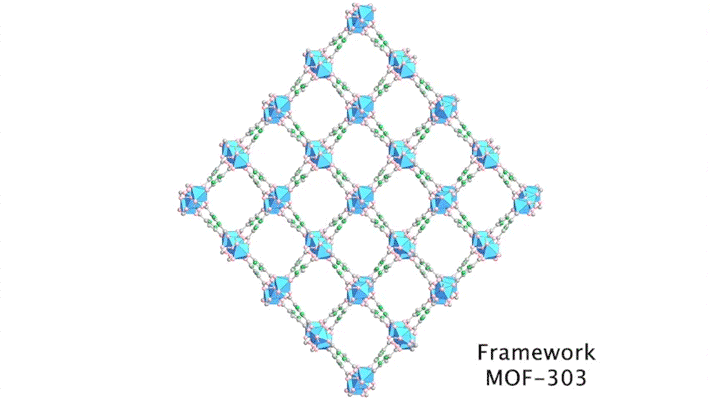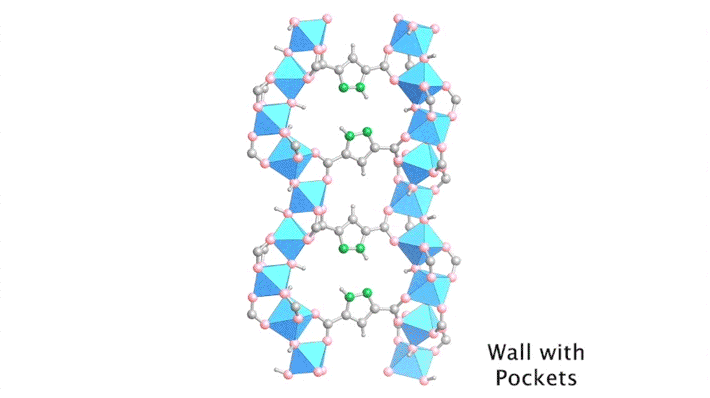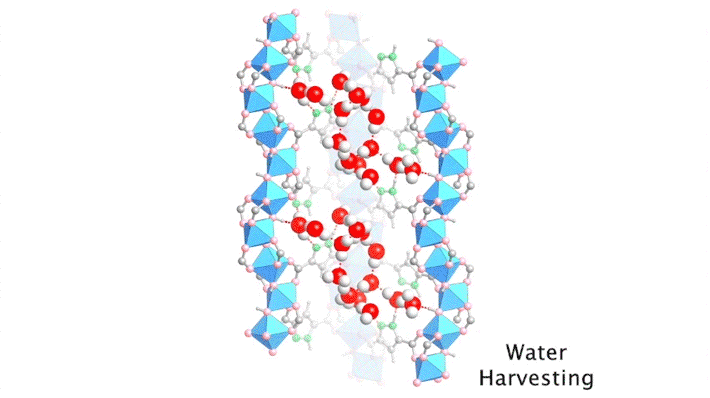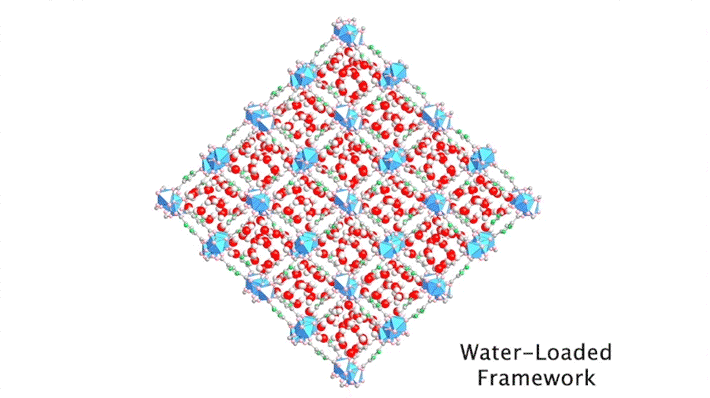
Researchers traced the step-by-step path of water-molecule uptake in a porous compound, then made pinpoint modifications to shape the material’s water-sorption behavior. The results led to improvements in the compound’s efficiency at harvesting water from the air, an important step toward alleviating water shortages in the future. Read more »![]()
![]()
Interlayer Coupling Drives Mysterious Phase Transition
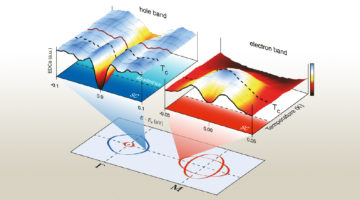
Researchers found that a mysterious phase transition in an iron-based superconductor is driven by interactions between the material’s 2D layers. The results counter the assumption that interlayer coupling is negligible in such materials, suggesting instead that the interactions can be an effective way to tune superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
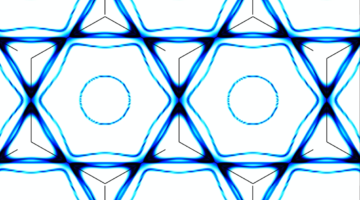
Scientists Discover ‘Secret Sauce’ Behind Exotic Properties of New Quantum Material
Kagome metals have long mystified scientists for their ability to exhibit collective behavior when cooled below room temperature. A research team has discovered that the kagome electrons’ unusual synchronicity is due to another behavior known as an electronic singularity, or the Van Hove singularity, which involves the relationship between the electrons’ energy and velocity. Read more »
Dramatic Conformer-Dependent Reactivity of the Acetaldehyde Oxide Criegee Intermediate with Dimethylamine Via a 1,2-Insertion Mechanism
Acetaldehyde-oxide (CH3CHOO) is an atmospherically pertinent reactive intermediate that exists in syn (right) and anti (left) conformational forms. Experiment and theory reveal that the reaction of anti with dimethylamine is several orders of magnitude faster than that of syn with dimethylamine, despite both reactions being energetically downhill. Read more »
With a Little Help, New Optical Material Assembles Itself
Researchers have demonstrated that tiny concentric nanocircles self-assemble into an optical material with precision and efficiency. Electron microscopy and x-ray scattering revealed the structure and spatial distribution of each ingredient in the resulting materials. The new findings could enable the large-scale manufacturing of multifunctional nanocomposites. Read more »
A {Ni12}-Wheel-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Coordinative Binding of Sulphur Dioxide and Nitrogen Dioxide
SO2 and NO2 are important air pollutants, and understanding the mechanism of capture materials drives the development of new clean-up technologies. In situ synchrotron x-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic experiments were used to establish a detailed molecular mechanism consisting of reversible coordination of SO2 and NO2 at the six open NiII sites on the unprecedented {Ni12}-wheel of a robust metal–organic framework material at crystallographic resolution. Read more »
Hardening Effects in Superhard Transition-Metal Borides
Novel superhard materials with exciting potential for applications in cutting tools and abrasives can be designed by combining incompressible transition metals with boron to create phases like WB4, pictured here. Diamond-cell-based high-pressure radial diffraction enables the direct study of lattice specific mechanisms for hardening. Read more »
ALS in the News (January 2022)
-
-
-
- COVID: How one person’s cells led to our only antibody treatment for omicron
- Physicists discover ‘secret sauce’ behind exotic properties of new quantum material
- Secondary structures in DNA are associated with cancer
- Berkeley Lab’s top 10 science stories of 2021
- New technique visualizes every pigment cell of zebrafish in 3D
- New device advances commercial viability of solar fuels
- Visualising cell structures in three dimensions in mere minutes
-
-
Synergistic Engineering of Side Chains and Backbone Regioregularity of Polymer Acceptors for High-Performance All-Polymer Solar Cells with 15.1% Efficiency
Researchers developed a series of polymer acceptors with controlled backbone regioregularities and side chain structures. All-polymer solar cells based on a RRg-C20 acceptor which has a regioregular backbone and optimal side chain length achieve a high power conversion efficiency of 15.12%, attributed to high electron mobility and optimal blend morphology. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- …
- 83
- Next Page »