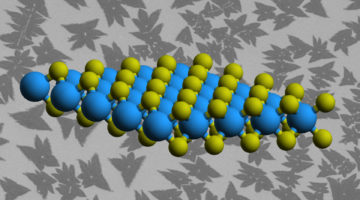
Researchers combined a toolbox of techniques to home in on natural, nanoscale defects formed in the manufacture of monolayer WS2, measuring their electronic effects in detail not possible before. The latest result marks the first comprehensive study at the ALS involving nanoARPES, which researchers enlisted to probe the 2D samples with x-rays. Read more »
Plumbing the Depths of Interfaces and Finding Buried Treasure
Understanding the interfaces where solids and liquids meet is key to controlling a wide range of energy-relevant processes, from how batteries store energy to how metals corrode, and more. Now researchers have explored such interfaces and found what they describe as a treasure trove of unexpected results that expands our understanding of working interfaces and how to probe them. Read more »
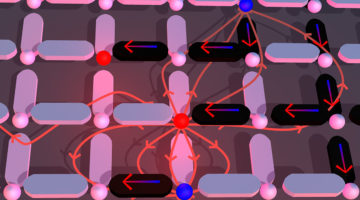
How to Catch a Magnetic Monopole in the Act
A research team has created a nanoscale “playground” on a chip that simulates the formation of exotic magnetic particles called “monopoles.” The study could unlock the secrets to ever-smaller, more powerful memory devices, microelectronics, and next-generation hard drives that employ the power of magnetic spin to store data. Read more »
Meteorites Suggest Galvanic Origins for Martian Organic Carbon
Nanoscale analyses of Martian meteorites suggest that organic carbon on Mars may have been formed by electrochemical reactions between briny liquids and volcanic minerals, as might occur in a galvanic cell. The study has major implications for astrobiology and could also shed light on the reactions that led to life on the early Earth. Read more »
ALS Tips Hat to 10 Years of Top-Off
In February, the ALS marked the 10th anniversary of one of the biggest upgrades in its history: the transition to “top-off mode,” which took place on February 11, 2009. To celebrate, the ALS community gathered for ring-shaped pastries (i.e., donuts) and coffee (topping off allowed). Brief remarks were given by Steve Kevan and Dave Robin. Read more »
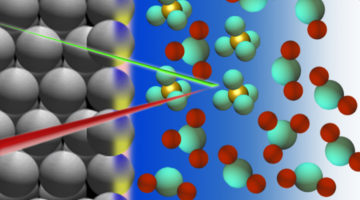
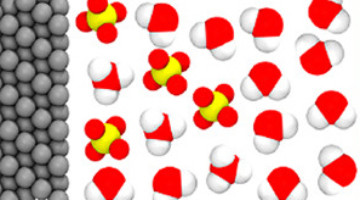
Getting to the Bottom of a Metal/Acid Interface
Researchers identified the molecules that collect at the interface between a platinum electrode and an acidic electrolyte under an applied voltage. Knowledge of the structure and composition of such nanometer-thin interface regions is key to understanding topics such as corrosion, geochemistry, electrocatalysis, and energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
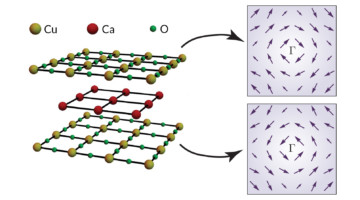
Spin-Momentum Locking in Cuprate High-Temperature Superconductors
A form of spin-momentum locking, similar to the strong linkage between electron spin and momentum in topological insulators, has been found in a cuprate superconductor. The results open a new chapter in the mystery of high-temperature superconductors, suggesting that new, unexplored interactions and mechanisms might be at play. Read more »![]()
![]()
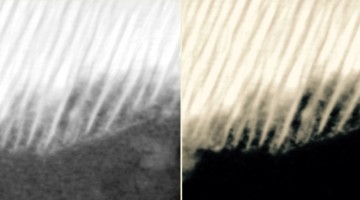
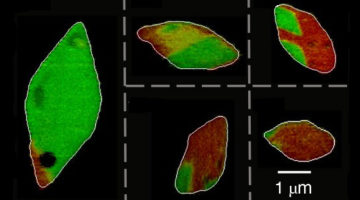
Hidden Flow of Lithium Ions Points Way to Better Batteries
Experiments revealed that lithium ions unexpectedly flow along the surfaces of electrode particles, boosting the growth of lithium “hot spots” that shorten battery life. The results correct decades’ worth of assumptions and will help improve battery design, potentially leading to a new generation of lithium-ion batteries. Read more »![]()
Forum Reinforces ALS Links to Water-Energy Nexus
About 80 Berkeley Lab scientists gathered at the ALS last week for an “ALS Water-Energy Outreach Forum” to discuss the challenges and opportunities arising from a growing focus on the nexus between water and energy—two resources essential to human populations—and to explore how the ALS can help address key questions in the field. Read more »
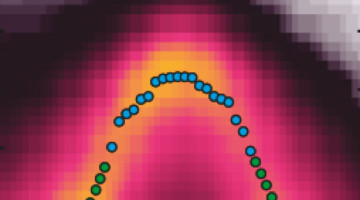
Electric-Field Switching of Topological Phase
Researchers have successfully switched a topological insulator on and off by applying an electrical field. The work represents a major advancement toward the creation of a functioning topological transistor that would allow devices to operate more efficiently at lower power than conventional electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- …
- 83
- Next Page »