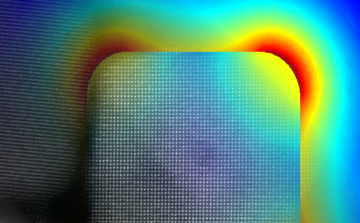
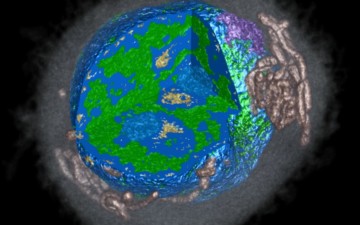
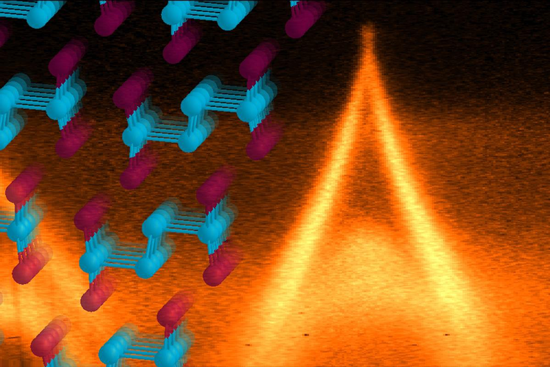
Using synchrotron infrared nanospectroscopy (SINS) at the ALS, researchers have for the first time probed infrared plasmonic excitations in single nanocrystals. This allowed the pinpointing of dopant effects on an emerging class of materials with potential for molecular-sensing and energy-harvesting applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALSNews Vol. 375
ALSNews Monthly Newsletter of the Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory New Catalyst Boosts Selective Formation of Olefins from Syngas Experiments at the ALS have helped to explain how a new catalyst significantly boosts the selective formation of light olefin molecules—important building blocks in the petrochemical industry—from syngas. The new process could allow forRead More Read more »
ALSNews Vol. 374
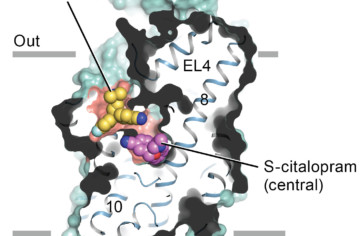
ALSNews Monthly Newsletter of the Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory How Antidepressants Block Serotonin Transport Malfunctions in the complex protein “machinery” of serotonin transport can result in depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, aggression, anxiety, and Parkinson’s disease. Now, researchers have obtained x-ray crystallographic structures of the difficult-to-crystallize human serotonin transporter bound to two commonly prescribedRead More Read more »
How Antidepressants Block Serotonin Transport
Malfunctions in the complex protein “machinery” of serotonin transport can result in depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, aggression, anxiety, and Parkinson’s disease. Now, researchers have obtained x-ray crystallographic structures of the difficult-to-crystallize human serotonin transporter bound to two commonly prescribed antidepressant drug molecules. Read more »![]()
![]()
Getting to the Root of Grapevine Hydraulics
In grapevines, “root pressure” was assumed to play a role in recovering from embolisms (blockages) in a plant’s water-transport systems during drought conditions. To clarify this, researchers used ALS Beamline 8.3.2 to obtain 3D microtomographic images of grapevine stem segments detached from roots and leaves. Read more »
New Insights into Oxygen’s Role in Lithium Battery Capacity
Researchers working at the ALS have recently made new discoveries in understanding the nature of charge storage in lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, opening up possibilities for new battery designs with significantly improved capacity. Looking at a popular Li-rich cathode material, the researchers used soft x-ray techniques to quantifiably explain oxygen’s role in Li-ion charge capacity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Mapping the Topology of the Human Genome
To determine how a gene will function, we need to know the spatial arrangement of the genome in the nucleus. Researchers have made a significant advance in determining this 3D organization by combining modeling and probabilistic calculations with minimally perturbing imaging techniques. Read more »
High spatial resolution mapping of chemically-active self-assembled N-heterocyclic carbenes on Pt nanoparticles
Many functional materials (e.g. catalysts) critically depend on the spatial distribution of surface active sites. However, most spectroscopic measurements are ensemble-based, where reactivity is averaged over millions of nanoparticles. Here, carbene attached to nanoparticle surfaces serves a model system for studying catalytic reactions on single nanoparticles. Read more »
Nanocrystals in compression: unexpected structural phase transition and amorphization due to surface impurities
We report an unprecedented surface doping-driven anomaly in the compression behaviors of nanocrystals. The results suggest that the physical properties of the interior of nanocrystals can be controlled by the surface, providing an unconventional and new degree of freedom in search for nanocrystals with novel tunable properties that can trigger applications in multiple areas of industry and provoke more related basic science research. Read more »
A Novel Quasi-1D Topological Insulator
The tantalizing prospect of energy-saving, ultralow-power electronics has led to a vigorous search for optimal topological insulator materials. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered the first of a new class of topological insulators with unique properties: quasi-1D bismuth iodide. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- …
- 83
- Next Page »