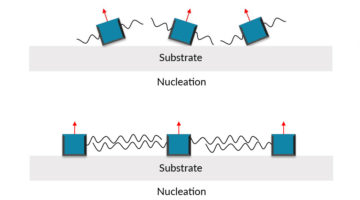
Perovskite thin films have many attractive properties for use in photovoltaics, but their assembly into practical devices has led to trade-offs between efficiency and stability. The addition of surfactant-type molecules with hydrophobic chains helped produce perovskite solar cells that are both efficient and stable. Read more »
Off the Scales: Fish Armor Both Tough and Flexible
Humans have drawn technological inspiration from fish scales going back to ancient times: Romans, Egyptians, and other civilizations would dress their warriors in scale armor, providing both protection and mobility. Now, scientists have characterized carp scales down to the nanoscale, enabling them to understand how the material is resistant to penetration while retaining flexibility. Read more »
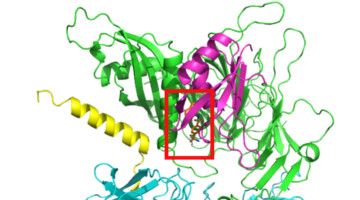
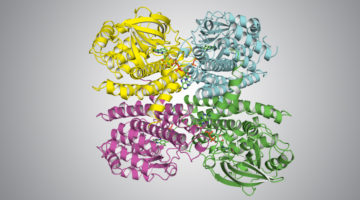
How a Cancer Drug Targets Proteins for Degradation
Protein structures obtained by Novartis researchers helped reveal how a cancer drug promotes the degradation of proteins essential to cell proliferation. A detailed understanding of the drug’s mechanism of action is key to determining whether the protein-degradation system can be reprogrammed to degrade different targets. Read more »![]()
Jin Qian, Theoretical and Computational Chemistry Postdoc
As a theoretical chemist, Jin Qian builds “virtual universes” that help predict what experimental chemists will see in their research. She focuses on water formation, a theme that carries through to one of her hobbies, which she is sharing with us in this month’s postdoc profile. Read more »
Masks On, Ready to Work: Meet the People Supporting COVID-19 Science
David Richardson’s job is literally to make sure the light stays on. But it’s not just any light—it’s a very special x-ray light that could play a crucial role in an eventual treatment for COVID-19. Richardson is an operator at the ALS, and is one of a handful of workers providing essential services to scientists working on COVID-19-related research. Read more »
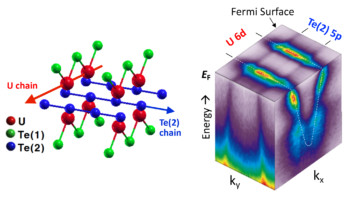
A Forked Path for Superconductivity
Uranium ditelluride (UTe2) exhibits a form of superconductivity that could, in theory, enable fault-tolerant quantum computing. Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy revealed several aspects of the material’s unusual electronic environment, including one-dimensional conducting channels that are orthogonally oriented. Read more »
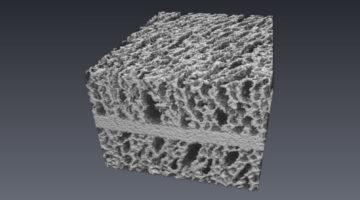
Porous Electrolyte Frameworks for All-Solid-State Batteries
With the help of microtomography at the ALS, researchers developed a method to produce a porous electrolyte framework that they used to construct a working all-solid-state battery. Such batteries potentially offer a higher energy density, longer cycle life, and better inherent safety than state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
Study Leads to Firmer Grasp of Biochemical “Reactive Handle”
Protein crystallography provided new insight into a functional group of molecules that, if added to bacterial enzymes, could enable a variety of alterations to the bacteria’s polymer output. Tweaking enzymes to produce these “reactive handles” is a first step toward biosynthesizing diverse polymers with tailored properties. Read more »
Jason Jed, Systems Manager
Before Jason Jed joined the ALS last month, he had already toured the facility in person and through virtual reality. Is it any wonder that he knows some of the more hidden rooms at the ALS? Read more »
Seeing ‘Under the Hood’ in Batteries
To push battery performance, researchers want to learn how the individual ingredients of battery materials behave beneath the surface. But many techniques only scratch the surface of what’s at work inside batteries. A high-sensitivity x-ray technique is attracting a growing group of scientists because it provides a deeper, more precise dive into battery chemistry. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- …
- 28
- Next Page »