Johanna Nelson Weker, UEC chair, celebrates a successful User Meeting. She encourages the user community to get involved by submitting feedback or even joining the UEC. Keep an eye out for the call for new member nominations. Read more »
All News & Updates
U.S. Energy Secretary Granholm Visits Berkeley Lab
In a visit to Berkeley Lab on August 20, Secretary Granholm and Congresswoman Barbara Lee met doctoral fellow Mikayla Barry at ALS Beamline 9.3.1. They also heard about extreme ultraviolet lithography and how protein crystallography enabled critical COVID research and Jennifer Doudna’s work on CRISPR. Read more »
A Powerful Infrared Technique Broadens Its Horizons
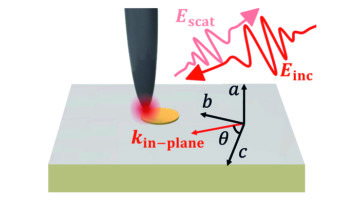
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) focuses infrared light to dimensions below the diffraction limit, measuring properties with components perpendicular to the sample surface. Researchers have now devised a way to probe components parallel to the sample, where the technique has been less sensitive. Read more »
Machine-Learning Team Receives 2021 Halbach Award
This year’s Halbach Award for Innovative Instrumentation at the ALS went to a team of accelerator physicists and computer scientists who were able to use machine-learning techniques to solve a problem that has plagued third-generation light sources for a long time: fluctuations in beam size due to the motion of insertion devices. Read more »
Autonomous Data Acquisition for Scientific Discovery
Researchers at large scientific facilities such as the ALS have applied a robust machine-learning technique to automatically optimize data gathering for a variety of experimental techniques. The work promises to enable experiments with large, complex datasets to be run more quickly, efficiently, and with minimal human intervention. Read more »![]()
![]()
2021 Renner Award winner Andrea “Andi” Jones
At this year’s ALS User Meeting, Andrea “Andi” Jones, proposal coordinator in the User Services Office, was honored with the 2021 Tim Renner User Services Award. The ALS Users’ Executive Committee selected Jones for “her dedication and commitment in supporting the User Office that have allowed efficient proposal reviews and beamtime allocations during the pandemic.” Read more »
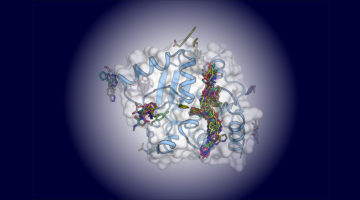
Functional and structural characterization of AntR, an Sb(III) responsive transcriptional repressor
Antimony is considered a priority environmental pollutant by the EPA. The ant operon of the antimony-mining bacterium, C. testosterone, confers resistance to Sb(III). The operon is regulated by the product of the first gene in the operon, antR. This is the first report of the structure and binding properties of antR, with high selectivity for environmental antimony. Read more »
Sifting through Fragments for COVID-19 Treatments
COVID-19 vaccines are essential for preventing serious disease, but the identification of new drugs is still necessary for the treatment of patients who become sick as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, scientists used computational docking and crystallography to screen large numbers of small molecules for potential use in drug compounds. Read more »
September 1 Proposal Deadline and COVID updates
The ALS is committed to supporting the science of our users, and we’re looking forward to welcoming back more on-site users this fall while continuing to support remote experiments. Please review the requirements for access to the ALS and remember to submit your proposals for the next cycle by 11:59 p.m. Pacific on September 1. Read more »
This Exotic Particle Had an Out-of-Body Experience; These Scientists Took a Picture of It
Scientists have taken the clearest picture yet of electronic particles that make up a mysterious magnetic state called a quantum spin liquid (QSL), in which electrons decompose into spin-like particles (spinons) and charge-like particles (chargons). The achievement could facilitate the development of superfast quantum computers and energy-efficient superconductors. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- …
- 139
- Next Page »