Researchers have developed a fast, systematic way to get the best performance out of x-ray mirrors by optimizing their positioning in beamlines. The system does in a day what used to take many days, by combining precise surface metrology with computer analysis of the optimal alignment of a mirror in a beamline. Read more »
All News & Updates
Study Concludes Glassy Menagerie of Particles in Beach Sands Near Hiroshima is Fallout Debris from A-Bomb Blast
Mario Wannier was methodically sorting through particles in samples of beach sand from Japan’s Motoujina Peninsula when he spotted something unexpected: a number of tiny, glassy spheres and other unusual objects. X-ray studies have provided evidence that they are A-bomb fallout from the destroyed city of Hiroshima. Read more »
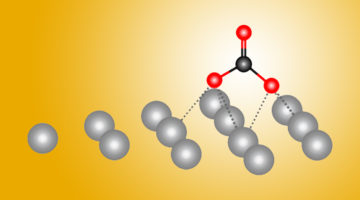
A New Path to Carbon Dioxide Transformation
Combining ALS experiments with quantum-mechanical calculations, scientists found dramatic differences in how carbon dioxide (CO2) reactions begin on silver as opposed to copper. Both metals help transform CO2—a greenhouse gas—into more useful forms, and this new atomic-level data could help make the process more efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
Self-Assembling 2D Arrays with de Novo Protein Building Blocks
Modular self-assembly of biomolecules in two dimensions (2D) is straightforward with DNA but has been difficult to realize with proteins, due to the lack of modular specificity similar to Watson–Crick base pairing. Here, researchers describe a general approach to designing 2D arrays using de novo designed pseudosymmetric protein building blocks. Read more »
Exploring the “minimal” structure of a functional ADAMTS13 by mutagenesis and small-angle X-ray scattering
Researchers used the SIBYLS beamline to gain insight into ADAMTS13, the only known protein to regulate the adhesive function of von Willebrand factor (VWF), a blood-clotting protein. When VWF is deficient or abnormal, it causes a common inherited bleeding disorder, von Willebrand disease. VWF is also implicated in arterial and deep-vein thrombosis, stroke, atherosclerosis, sickle cell crisis, and sepsis. Read more »
Dylan McReynolds, Computer Systems Engineer
Dylan McReynolds joined the ALS Computing Program in February. After spending 25 years working in industry, he is excited to meet beamline scientists and users to understand and support their software needs. Read more »
ALS Director Announces Andreas Scholl as New Science Deputy
I am delighted to inform you that our search for a new science deputy has ended successfully with the appointment of ALS senior staff scientist Andreas Scholl. I look forward to working with him as we continue to manage this world-leading facility and get ready for ALS-U science. Read more »
Design and Synthesis of Selective Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Allosteric Inhibitors for the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome and Other Brain Disorders
PDE4D enzymes are important for normal brain function. Mutations have been asssociated with an ultrarare neurodevelopmental disorder, and genetic variation in PDE4D contributes to biological variation in human cognitive ability. Here, researchers report on novel PDE4D inhibitors providing potent memory-enhancing effects in a mouse model, with improved tolerability and reduced vascular toxicity over earlier PDE4 inhibitors. Read more »
Chiral Crystals Give Rise to Topological Conductors
Researchers have discovered materials whose chiral crystal structures produce chirality in their electronic behavior. These topological conductors retain their unique electronic properties regardless of defects and open new possibilities in materials research. Read more »
April 2019 Message from the UEC
Fanny Rodolakis, the chair of the Users’ Executive Committee (UEC) for 2019, reports on the most recent UEC meeting and calls for speaker suggestions for this year’s User Meeting. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- …
- 139
- Next Page »