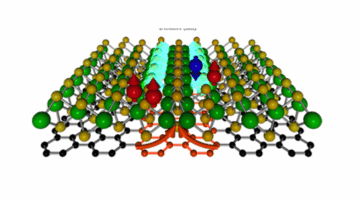
A research team used the ALS to recreate how the Sun breaks apart nitrogen to inform a new model that can be used to understand the fate of a variety of elemental isotopes to explain atmospheric evolution on planets across the solar system. Read more »
Science Briefs
Separating an Electron into Waves of Spin and Charge
Researchers are exploring how a thin film can host a Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid, which separates an electron’s charge and spin. The research findings could contribute to the development of ultra-compact and energy-efficient technologies. Read more »
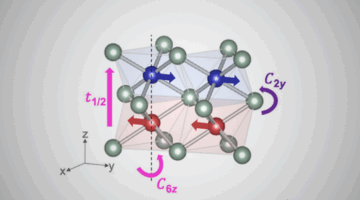
The Quest for an Altermagnet
Researchers determine the unique electronic structure of altermagnets, which offers numerous benefits in creating energy-efficient devices based on spin-polarized electron currents. Understanding how altermagnetism works could contribute to the development of next-generation memory, logic, or sensing devices that are faster and consume less power. Read more »
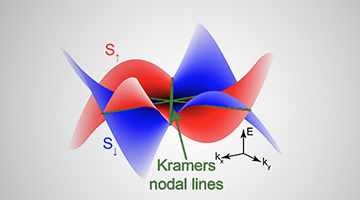
Designing Quantum Materials for Future Electronics
Researchers bring theory into practice and confirm a new material’s characteristics at the ALS. The study opens new opportunities to design a substance that renders extra “handles” on the electron—not just its charge, but its spin and valley—so we can build computers that are faster, cooler, and more energy-efficient compared to traditional electronics. Read more »
Dehydration Key Element in Soil Microbe Evolution
A new study illustrates how microbes respond, in real time, to environmental stress, improving the research community’s knowledge of the hidden microbial engines that keep our planet running. Read more »
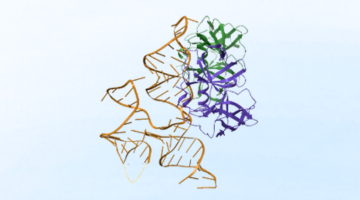
Researchers Identify Viral Swiss Army Knife, Clarifying How Replication Occurs
Viruses are ingenious, infectious agents, capable of replicating inside the living cells of a host organism. Enterovirus, a common viral pathogen, is responsible for a range of diseases from mild colds to severe conditions, including viral meningitis, myocarditis, and paralysis. A new study sheds light on how enteroviruses use structured RNA elements and multifunctional proteins to coordinate viral replication efficiently using minimal genetic material. Read more »
Efficient Upcycling of Plastic Waste into Useful Liquid Fuels
Researchers found a way to turn single-use plastics (e.g., grocery bags and packaging) into useful liquid fuels, like components of gasoline or diesel, without needing high heat, rare metals, or added chemicals. The work presents a promising pathway to address the global plastic waste crisis, with both environmental and economic advantages. Read more »
ALS Captures Structure of Engineered Protein, Opening New Options to Treat IBD
Researchers use the ALS to confirm the structure of an engineered immune protein that could open new opportunities to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Read more »
A Deeper Look into Emergent Magnetism at Interfaces
Researchers shed new light on interfacial ferromagnetism in superlattices of alternating magnetic layers. By advancing our understanding of atomic-level interactions at magnetic interfaces, this work expands the scope of traditional interface studies and lays the groundwork for future innovations in magnetic storage and spintronics. Read more »
Building a Gated-Access Fast Lane for Ions
In organic conductors where charge is carried by both electrons and ions, scientists have discovered a way to make the ions move more than ten times faster than in comparable ion-transport methods. The results could apply to a host of areas, including improved battery charging, biosensing, soft robotics, and neuromorphic computing. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 23
- Next Page »