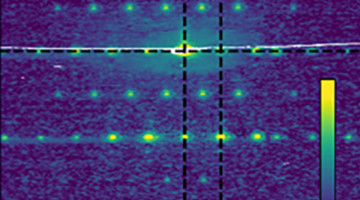
Researchers fabricated artificial spin lattices that undergo a paramagnetic-to-antiferromagnetic phase transition. These artificial antiferromagnets enable studies of dynamical properties that are critical to understanding, and ultimately implementing, real-world applications such as advanced computing and data-storage technologies. Read more »
Science Briefs
COSMIC Probes Evolution of Single-Atom Platinum Catalyst
Researchers synthesized a single-atom platinum catalyst that outperformed, by a factor of 15, conventional platinum-based catalysts, which are used for fuel cells and automotive emissions control. Operando x-ray spectromicroscopy at the ALS’s COSMIC beamline revealed how electronic interactions affect the material’s morphology. Read more »
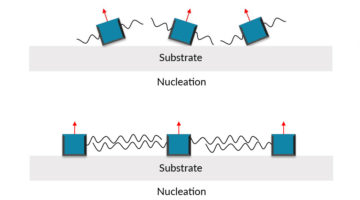
Long Chains Stabilize Higher-Efficiency Solar Cells
Perovskite thin films have many attractive properties for use in photovoltaics, but their assembly into practical devices has led to trade-offs between efficiency and stability. The addition of surfactant-type molecules with hydrophobic chains helped produce perovskite solar cells that are both efficient and stable. Read more »
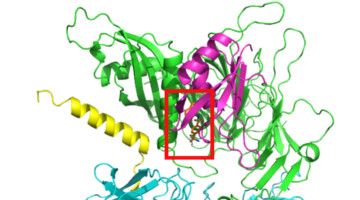
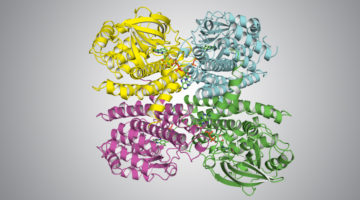
How a Cancer Drug Targets Proteins for Degradation
Protein structures obtained by Novartis researchers helped reveal how a cancer drug promotes the degradation of proteins essential to cell proliferation. A detailed understanding of the drug’s mechanism of action is key to determining whether the protein-degradation system can be reprogrammed to degrade different targets. Read more »![]()
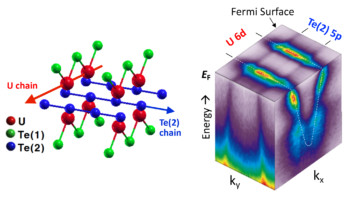
A Forked Path for Superconductivity
Uranium ditelluride (UTe2) exhibits a form of superconductivity that could, in theory, enable fault-tolerant quantum computing. Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy revealed several aspects of the material’s unusual electronic environment, including one-dimensional conducting channels that are orthogonally oriented. Read more »
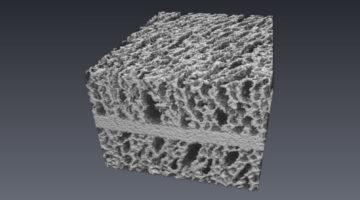
Porous Electrolyte Frameworks for All-Solid-State Batteries
With the help of microtomography at the ALS, researchers developed a method to produce a porous electrolyte framework that they used to construct a working all-solid-state battery. Such batteries potentially offer a higher energy density, longer cycle life, and better inherent safety than state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
Study Leads to Firmer Grasp of Biochemical “Reactive Handle”
Protein crystallography provided new insight into a functional group of molecules that, if added to bacterial enzymes, could enable a variety of alterations to the bacteria’s polymer output. Tweaking enzymes to produce these “reactive handles” is a first step toward biosynthesizing diverse polymers with tailored properties. Read more »
Survival of T. rex Microvascular Structures from Deep Time
Researchers used several analytical techniques at the ALS to demonstrate how soft-tissue structures may be preserved in dinosaur bones, countering long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts cannot survive more than one million years. Read more »
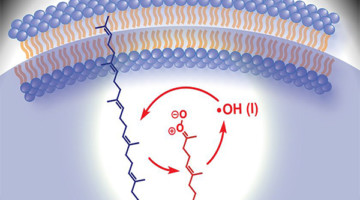
Criegee Intermediates Play Unexpected Role in Cell Chemistry
Researchers employed mass spectrometry to illuminate lipid nanodroplets under ultraviolet light. The results unexpectedly showed that hydroxyl radicals cause damage to cells via the formation of Criegee intermediates: molecules first proposed in 1975 to explain how pollutants react with the ozone layer in our atmosphere. Read more »
Can Minerals in the Earth’s Lower Mantle Store Water?
Earth is considered a watery planet, simply by virtue of the fact that 71% of its surface is covered by oceans. But researchers have discovered that, in the massive volume of material in Earth’s interior, minerals can serve as an important water reservoir, providing a new perspective on our planet’s water budget. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- …
- 23
- Next Page »