Scientists paired ferroelectric and ferrimagnetic materials so that their alignment can be controlled with a small electric field at near room temperatures, a major step in the development of ultralow-power microprocessors, storage devices, and next-generation electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
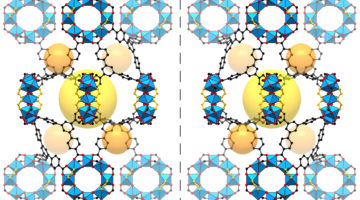
A New Way to Determine the 3D Structure of Molecules
Researchers have created a sort of nanoscale display case that enables new atomic-scale views of hard-to-study chemical and biological samples. The work could help to reveal new structural details for a range of challenging molecules by stabilizing them inside sturdy structures known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Read more »![]()
![]()
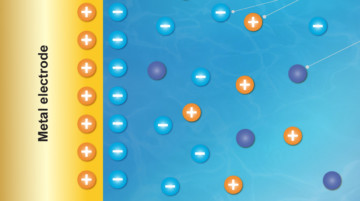
Tender X-Rays Map the Double-Layer Potential
In a first-of-its-kind experiment, ALS researchers demonstrated a new, direct way to study the inner workings of a phenomenon in chemistry known as an “electrochemical double layer” that forms where liquids meet solids—where battery fluid meets an electrode, for example. Read more »![]()
![]()
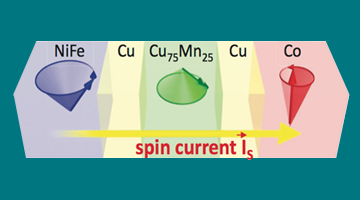
How to Directly Probe ac Spin Currents
Scientists working at the ALS have made the first unambiguous, direct measurements of ac spin currents flowing through nanostructured metal layers. The work represents a crucial step toward the development of future spintronic devices that are smaller, faster, and more energy efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
Molecular Switch Triggers Bacterial Pathogenicity
Using an array of high-powered x-ray imaging techniques at the ALS, scientists have revealed for the first time the molecular steps that turn on bacteria’s pathogenic genes. The study could open up new avenues in the development of drugs to prevent or treat bacterial infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Surface Treatment for Improving Fuel-Cell Cathodes
Solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) are a promising path toward the “clean” conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy with little or no carbon dioxide emission. With the help of the ALS, researchers from MIT recently found a way to treat SOFC cathode surfaces so that they perform better and last longer. Read more »![]()
![]()
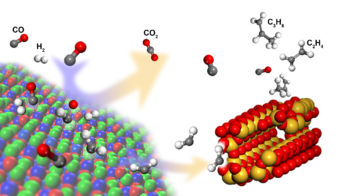
New Catalyst Boosts Selective Formation of Olefins from Syngas
Experiments at the ALS have helped to explain how a new catalyst significantly boosts the selective formation of light olefin molecules—important building blocks in the petrochemical industry—from syngas. The new process could allow for the use of alternative syngas feedstocks that save water and energy. Read more »![]()
![]()
SINS Reveals Dopant Effects in Plasmonic Materials
Using synchrotron infrared nanospectroscopy (SINS) at the ALS, researchers have for the first time probed infrared plasmonic excitations in single nanocrystals. This allowed the pinpointing of dopant effects on an emerging class of materials with potential for molecular-sensing and energy-harvesting applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
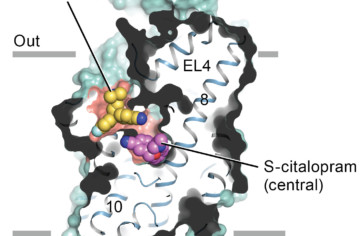
How Antidepressants Block Serotonin Transport
Malfunctions in the complex protein “machinery” of serotonin transport can result in depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, aggression, anxiety, and Parkinson’s disease. Now, researchers have obtained x-ray crystallographic structures of the difficult-to-crystallize human serotonin transporter bound to two commonly prescribed antidepressant drug molecules. Read more »![]()
![]()
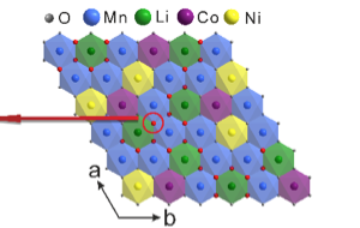
New Insights into Oxygen’s Role in Lithium Battery Capacity
Researchers working at the ALS have recently made new discoveries in understanding the nature of charge storage in lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, opening up possibilities for new battery designs with significantly improved capacity. Looking at a popular Li-rich cathode material, the researchers used soft x-ray techniques to quantifiably explain oxygen’s role in Li-ion charge capacity. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- …
- 27
- Next Page »