The atmosphere above the Amazon basin teems with biological particles that help form clouds. Because they break down in the Amazon’s high humidity, their origins are difficult to trace. Containing the same elements as sea salt, the particles were long thought to have blown in from the Atlantic Ocean, over 1200 kilometers away. However, researchers have found that much of the sodium in the air had a much more local source: fungal spores. The discovery that fungal spores contribute to the salt content in the atmosphere is a step forward in understanding their impact on tropical rainforest ecosystems around the world.
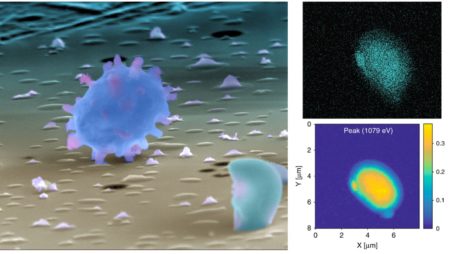
Researchers collected fungal spores from the Amazon rainforest and examined them using scanning transmission x-ray microscopy with near-edge x-ray absorption fine structure analysis (STXM/NEXAFS) at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) and other chemical imaging techniques at the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. X-ray microscopy at Beamline 11.0.2.2 demonstrated the high sodium content in the fungal spores. Further chemical imaging revealed that the high humidity conditions in the Amazon rainforest cause fungal spore particles to rupture and release submicrometer-to-micrometer sized salt fragments. Through modeling, the group determined that fungal spores contribute 30–60% of the “sea salt-like” particles in the region’s atmosphere.
Because these biological particles are central in cloud formation and scatter solar radiation, pinpointing their origin will improve climate models based on atmosphere–biosphere interactions. The impact stretches beyond the Amazon basin, uncovering atmospheric insights for other ecosystems, from tropical Malaysian rainforests to arid and frozen Antarctica.
China, S.M. Burrows, B. Wang, T.H. Harder, J. Weis, M. Tanarhte, L.V. Rizzo, J. Brito, G.G. Cirino, P.-L. Ma, J. Cliff, P. Artaxo, M.K. Gilles, and A. Laskin, “Fungal spores as a source of sodium salt particles in the Amazon basin,” Nat. Commun.9, 4793 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07066-4.