Researchers use the ALS to confirm the structure of an engineered immune protein that could open new opportunities to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Read more »
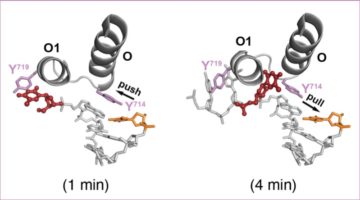
DNA Synthesis: Flip It and Reverse It
What if the current model for DNA synthesis were flipped on its head? Using time-resolved x-ray crystallography, researchers gained new insights into this essential biological process, revealing that two steps in the synthesis pathway are, in reality, reversed. Read more »
Structure-Based Design of Selective LONP1 Inhibitors for Probing In Vitro Biology
LONP1 is an AAA+ protease that maintains mitochondrial homeostasis by removing damaged or misfolded proteins. Elevated activity and expression promotes cancer cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis-inducing reagents. Herein, we report the development of selective boronic acid-based LONP1 inhibitors using structure-based drug design as well as the first structures of human LONP1 bound to various inhibitors. Read more »
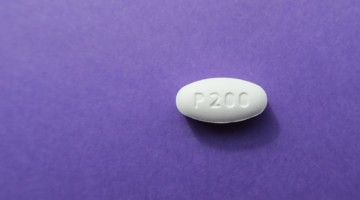
X-Ray Experiments Contribute to Studies of a Drug Now Approved to Combat Tuberculosis
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved a new antibiotic that, in combination with two existing antibiotics, can tackle one of the most formidable and deadly treatment-resistant forms of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. Studies exploring the structure and function of the new drug benefited from x-ray experiments at the ALS. Read more »
Design and Synthesis of Selective Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Allosteric Inhibitors for the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome and Other Brain Disorders
PDE4D enzymes are important for normal brain function. Mutations have been asssociated with an ultrarare neurodevelopmental disorder, and genetic variation in PDE4D contributes to biological variation in human cognitive ability. Here, researchers report on novel PDE4D inhibitors providing potent memory-enhancing effects in a mouse model, with improved tolerability and reduced vascular toxicity over earlier PDE4 inhibitors. Read more »
Structural Characterization of a Synthetic Tandem-Domain Bacterial Microcompartment Shell Protein Capable of Forming Icosahedral Shell Assemblies
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are subcellular compartments found in many prokaryotes, and they are of considerable interest for biotechnological applications. The BMC-H2 shell system constitutes a relatively simple generic building block that could be used to construct designed shells with a relatively highly tunable pore. Read more »
Structure-based Design of Pyridone–Aminal eFT508 Targeting Dysregulated Translation by Selective Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Interacting Kinases 1 and 2 (MNK1/2) Inhibition
Dysregulated translation drives key hallmarks of cancer and is controlled by Phase 2 candidate eFT508 binding to the MNK protein, exploiting stereoelectronic interactions, critical to the compound’s selectivity and potency. Read more »
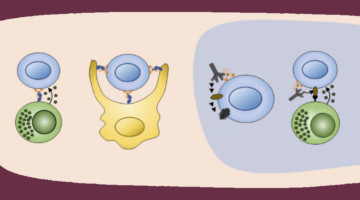
Modified Antibody Clarifies Tumor-Killing Mechanisms
An antibody was modified to activate a specific pathway of the immune system, demonstrating its value in killing tumor cells. The work provides a platform for disentangling different immune-system pathways and could lead to the design of improved immunotherapies. Read more »![]()
![]()
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »
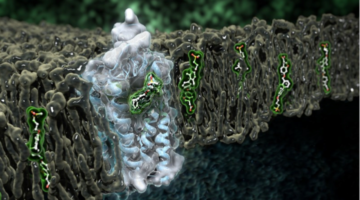
Takeda Advances Diabetes Drug Development at the ALS
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), characterized by abnormally high blood glucose levels, affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. In the pursuit to better treat this disease, the human receptor protein GPR40 has been identified by pharmaceutical company Takeda as a potential new drug target.