Researchers demonstrate current-driven magnetic skyrmion motion in van der Waals ferromagnets at room temperature. The skyrmion motion presents ultra-low critical current density to activate their dynamics, thanks to minimized defects in the van der Waals gap. The findings will provide a new platform for spintronics application in the future. Read more »
Magnetically Selective Versatile Transport of Microrobotic Carriers
Field-driven transport systems offer the possibility of biofunctionalized carriers for microrobotics, biomedicine, and cell delivery. Here, researchers show how magnetic fields may selectively manipulate and drive microrobotics along a patterned micromagnet. Different-sized magnetic carriers move in multiple directions, including selective rotation and bidirectional movement. Such steering systems can direct the delivery of drugs or cells into artificial microvascular channels. Read more »
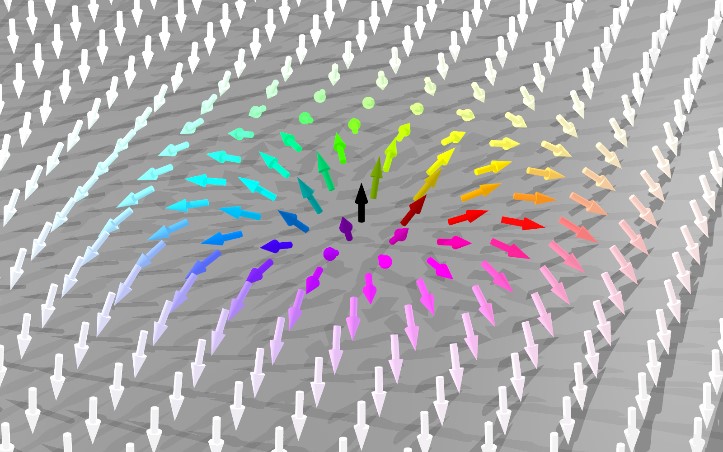
Skyrmion Creation and Annihilation Made Simple
Researchers developed a simple approach to writing and deleting skyrmions on demand, using heat and magnetic fields generated by an electrical current, by-products normally considered problematic. The ubiquitous character of these effects, coupled with simplicity of design, offers much-needed scalability and broad applicability. Read more »
Shape transformation and self-alignment of Fe-based nanoparticles
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have widespread applications in biotechnology, materials science, engineering, and environmental studies. Thus, much attention has been paid to their controllable synthesis. Three new functions of iron-based nanoparticles are reported: shape transformation, oxidation prevention, and self-alignment. Read more »
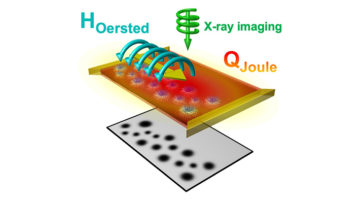
Magnetic Skyrmions: Current‐Induced Skyrmion Generation through Morphological Thermal Transitions in Chiral Ferromagnetic Heterostructures
Magnetic skyrmions are particle‐like chiral twists of the magnetization that promise advances in spin‐based data storage and logic device applications. In this article, researchers examine current‐induced generation of skyrmions in heavy‐metal/ferromagnet multilayers and show that Joule heat pulses can drive topological transitions in magnetic textures and enable skyrmion creation on nanosecond timescales. Read more »
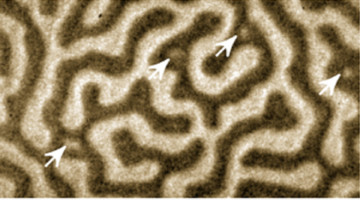
Ordered Magnetic Patterns in a Disordered Magnetic Material
Scientists have confirmed the presence of chirality, or handedness, in nanometers-thick samples of amorphous (noncrystalline) multilayer materials. The chirality—which potentially could be exploited to transmit and store data in a new way—was observed in the domain walls between neighboring regions of opposite spin. Read more »
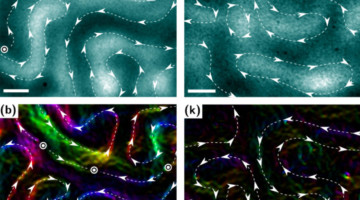
Experimental Evidence of Chiral Ferrimagnetism in Amorphous GdCo Films
Harnessing high‐resolution Lorentz microscopy, Robert Streubel and co‐workers visualize chiral ferrimagnetic domain walls in amorphous films, revealing a composition dependence that potentially enables a temperature control of intrinsic domain wall properties. The reconstructed electron phase (magnetic induction) of achiral Bloch domain walls is shown here. Read more »
Non-Crystal Clarity: Scientists Find Ordered Magnetic Patterns in Disordered Magnetic Material
Scientists have confirmed the presence chirality, or handedness, in nanometers-thick samples of amorphous (noncrystalline) multilayer materials. The chirality—which potentially could be exploited to transmit and store data in a new way—was observed in the domain walls between neighboring regions of opposite spin. Read more »
Driving Skyrmions Along a Racetrack
Researchers have demonstrated the ability to generate stable skyrmion lattices and to drive trains of individual skyrmions by short current pulses along a magnetic racetrack at speeds exceeding 100 m/s, as required for spintronic applications. Read more »
ALS, Molecular Foundry, and aBeam Technologies Collaborate to Make Metrology History
A collaboration between Bay Area company aBeam Technologies, the ALS, and the Molecular Foundry is bringing cutting-edge metrology instrumentation to the semiconductor market, which will enable a new level of quality control. Read more »![]()