The appropriately named diabolical ironclad beetle has an incredibly crush-resistant exoskeleton, which could serve as a blueprint for tougher materials. To see, in microscopic detail, what makes the beetle so uniquely ironclad, researchers used the ALS to explore a protective covering known as the “elytra,” its abdomen, and other parts. Read more »
Design and synthesis of high performance flexible and green supercapacitors made of manganese‐dioxide‐decorated alkali lignin
Researchers synthesized a plant‐based composite electrode for use in flexible supercapacitors and used synchrotron x‐ray microtomography to better understand the impact of microstructure and morphology on electrode porosity and electrical conductance. Read more »
Battery Breakthrough Gives Boost to Electric Flight and Long-Range Electric Cars
While lithium metal extends an EV’s driving range, it also shortens the battery’s useful life due to lithium dendrites that can cause short circuits. Researchers report a new class of soft, solid electrolytes—made from both polymers and ceramics—that suppress dendrites, before they can propagate and cause the battery to fail. Read more »
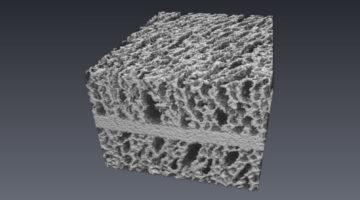
Porous Electrolyte Frameworks for All-Solid-State Batteries
With the help of microtomography at the ALS, researchers developed a method to produce a porous electrolyte framework that they used to construct a working all-solid-state battery. Such batteries potentially offer a higher energy density, longer cycle life, and better inherent safety than state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
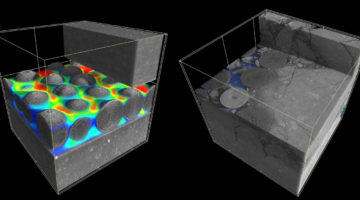
Direct Imaging of Fracture Closure in Reservoir Shales
Using x-ray microtomography at the ALS, researchers identified and characterized the microscale factors affecting fluid flow through shale fractures propped open with sand or ceramic spheres. A better understanding of propped fractures can lead to safer and more efficient recovery of hard-to-reach oil and gas resources. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Chemistry of Art
To learn more about the chemical processes involved in aging oil paints in microscopic and nanoscale detail, researchers conducted a range of studies that included 3D x-ray imaging of a paint sample. The study could have broader implications for conservation based on the observed chemistry of oil paints. Read more »
The Stomatopod Telson: Convergent Evolution in the Development of a Biological Shield
In this article, researchers identify multiscale structure‐mechanical property relationships within the shield-like exoskeletal telson structure of the mantis shrimp, used for defense and protection. Comparison of telsons from two evolutionarily divergent species reveal differences in macromorphology, cuticle thickness, and mineralization, imparting compressive stiffness as well as compliance for energy absorption. Read more »
Team Chemistry Powers Industry Collaborations at the ALS
At the ALS, industry users find scientific experts and specialized facilities. Their collaboration drives discovery in a variety of fields, yielding results that are greater than the sum of their parts. Read more »
Absorber Captures Excess Chemotherapy Drugs
Researchers have designed a biomedical device for absorbing excess chemotherapy drugs during cancer treatment, characterizing the active surface layer using x-ray microtomography. The work opens up a new route to fighting cancer that minimizes drug toxicity and enables personalized, targeted, high-dose chemotherapy. Read more »![]()
![]()
Comparative morphology of cheliceral muscles using high‐resolution X‐ray microcomputed‐tomography in palpimanoid spiders
Spiders are important predators in terrestrial ecosystems, yet we know very little about their principal feeding structures—the chelicerae—an extremely important aspect of spider biology. Here, using micro‐Computed‐Tomography scanning techniques, researchers perform a comparative study to examine cheliceral muscle morphology in six different spider specimens. Read more »