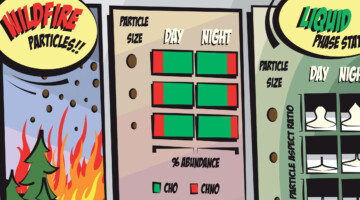
Researchers studied atmospheric aerosols influenced by wildfires in the Pacific Northwest. They examined the connection between particle size, chemical composition, and phase state, in particles collected during the day and at night. The information is important for modeling the effects of wildfire smoke on atmospheric properties. Read more »
Tracking the Breakdown of Cellulose at the Micron Scale
A time-resolved study using infrared spectromicroscopy in a carefully controlled environment revealed why enzymes get bogged down when trying to break up cellulose from plants. The work sheds new light on the challenge of extracting the sugars locked up in plants for use in making petroleum-free fuels, chemicals, and medicines. Read more »![]()
![]()
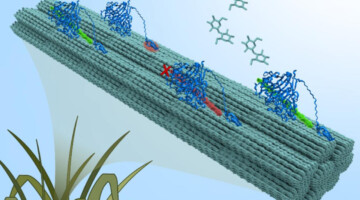
Watching the Enzymes that Convert Plant Fiber into Simple Sugars
Research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, and UC Davis sheds new light on how to access the sugars locked up in plants to produce petroleum-free fuels, chemicals, and medicines. The technique used combines a novel microfluidic device and infrared spectroscopy to study how a cellulose-degrading enzyme works in real time. Read more »
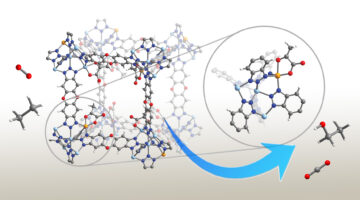
A Bio-Inspired Metal-Organic Framework for Capturing Wellhead Gases
Burning of natural gas at oil and gas wells, called flaring, is a major waste of fossil fuels and a contributor to climate change. In this work, researchers synthesized and characterized a metal-organic framework that uses biomimetic chemistry to convert wellhead gases into economically valuable feedstocks for petrochemical products. Read more »
Optical Properties of Individual Tar Balls in the Free Troposphere
Tar balls are found in biomass-burning smoke, and their sunlight-absorption properties are highly uncertain. This study investigates the optical properties of individual tar balls in the free troposphere to better understand their influence on climate. Read more »
Improving Carbon Retention in Grassland Soil from Point Reyes
Soil organic carbon directly influences the life-supporting services provided by soils, including the production of food and the regulation of atmospheric carbon dioxide. To better understand how minerals such as calcium affect carbon accumulation in soil, researchers studied soils collected from Point Reyes National Seashore. Read more »![]()
Case study evaluation of size-resolved molecular composition and phase state of carbonaceous particles in wildfire influenced smoke from the Pacific Northwest
Wildfires are significant sources of carbonaceous particles in the atmosphere. Given the dependence of atmospheric processes on particle physical and molecular properties, the interplay between particle size, phase state and chemical composition is investigated here for aerosols influenced by a 2021 Pacific Northwest wildfire event. Read more »
Making Renewable, Infinitely Recyclable Plastics Using Bacteria
Scientists engineered microbes to make the ingredients for recyclable plastics—replacing finite, polluting petrochemicals with sustainable alternatives. The new approach shows that renewable, recyclable plastics are not only possible, but also outperform those from petrochemicals. Read more »
New Pathway for SO2 Breakup Sheds Light on Earth’s Oxygenation
While calibrating a new scientific apparatus at the ALS, researchers discovered that ultraviolet light can break up sulfur dioxide (SO2) in a new way, with molecular oxygen (O2) as an unexpected product. The discovery sheds light on Earth’s Great Oxygenation Event 2.4 billion years ago, when atmospheric oxygen levels first began to rise. Read more »
Vestiges of the Early Solar System in Ryugu Asteroid
Samples returned to Earth from the asteroid Ryugu revealed that the building blocks of life formed 4.6 billion years ago in the extreme cold of space, followed by reaction with water. The dark, coal-like organic matter in the carbonaceous asteroid could have contributed to the formation of habitable planetary environments. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 8
- Next Page »