Vertical distribution of size-resolved chemical composition of Arctic aerosol particles was investigated in different cloud layers. Multimodal microspectroscopy analysis reveals a broadening of chemically-specific size distribution above the cloud top. Read more »
SO2 Photodissociation at 193 nm Directly Forms S(3P) + O2(3Σg–): Implications for the Archean Atmosphere on Earth
Sulfur isotope patterns in ancient rock layers inform our understanding of Earth’s Archean atmosphere. Before the Great Oxygenation Event (~2.4 billion years ago), hard ultraviolet light penetrated into the Earth’s surface, photodissociating sulfur dioxide directly to S + O2. This new product channel may help resolve discrepancies in the Earth’s evolutionary history. Read more »
Macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid (162173) Ryugu
We investigated the macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid Ryugu—brought to Earth by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft—measuring its elemental, isotopic, and functional group compositions along with its small-scale structures and morphologies. Analytical methods used included spectro-microscopies, electron microscopy, and isotopic microscopy. Read more »
An automated size and time-resolved aerosol collector platform integrated with environmental sensors to study the vertical profile of aerosols
Researchers present the vertical distribution of size-resolved aerosol composition over an agricultural site by deploying a newly developed lightweight automated size- and time-resolved aerosol collector (STAC) platform integrated with environmental sensors on unmanned aerial systems (e.g., tethered balloon systems). Read more »
New Insight into Titan’s Hazy Atmospheric Chemistry
Researchers simulated the complex chemistry that may be occurring in the hazy atmosphere of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, and analyzed the reaction products at the ALS. The work provided new insights into what future Titan probes may encounter upon arrival and what the atmosphere of Earth may have been like eons ago. Read more »
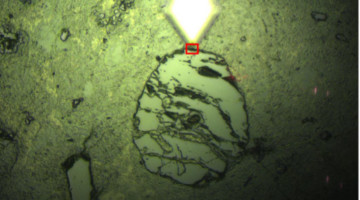
Nanoscale Infrared Study of Meteorite Mineralogy
Using a nanoscale infrared probe, researchers found that the minerals in a meteorite—an artifact representing the solar system’s past—were altered by water on very fine spatial scales. The work sheds light on conditions in the early solar system and lays groundwork for analyzing asteroid samples to be returned to Earth by NASA in 2023. Read more »![]()
![]()
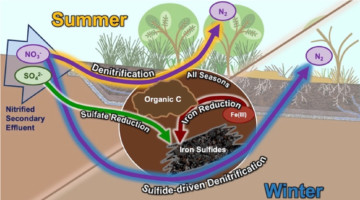
Removing Nitrogen from Wastewater using Horizontal Levees
Treated municipal wastewater often contains nitrogen, which has been linked to algal blooms that can devastate coastal ecosystems. In a recent study, researchers characterized the primary nitrogen-removal pathways in a horizontal levee, an engineered subsurface water-treatment system consisting of a gently sloping strip of land adjacent to storm-control levees. Read more »
Structural organization of the spongy mesophyll
Many leaves have two layers of photosynthetic tissue: the palisade and spongy mesophyll. The latter is not well characterized and often treated as a random assemblage of irregularly shaped cells. These results show that simple principles may govern the organization and scaling of the spongy mesophyll in many plants and demonstrate the presence of structural patterns associated with leaf function. Read more »
Biomineralization: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary history
In this review, Gilbert et al. develop a model for calcium carbonate biomineralization applicable to all phyla. Their model may help elucidate the key genetic components that drive biomineralization and offers insight into the consequences of global climate change on marine organisms. Read more »
How Iron Remediates Arsenic in Groundwater
Though iron has been demonstrated as an effective means to remediate arsenic contamination in groundwater, the mechanism was not well understood until now. For the first time, researchers have untangled the detailed steps of the interaction, informing more robust strategies for cleanup. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 8
- Next Page »