To explore what happens to minerals under the extreme conditions in Earth’s mantle, researchers developed an x-ray technique that bridges the gap between methods that reveal bulk properties and those that focus on individual crystals. Use of the technique has shed light on the dynamics of tectonic-plate subduction in Earth’s lower mantle. Read more »
Meteorites Reveal Magnetic Record of Protoplanet Churn
Researchers detected the signatures of ancient magnetic fields imprinted in the ferromagnetic grains of meteorites that originated from the same parent body. The results, combined with radioisotopic dating of the samples, support an extended time frame for the cooling of molten protoplanetary cores. Read more »
Scientists Design New Framework for Clean Water
A promising solution to water pollution from abandoned copper mines relies on materials that adsorb copper ions from wastewater, but commercially available products lack the required chemical specificity and load capacity. A team of scientists has designed a new crystalline material that targets and traps copper ions from wastewater with unprecedented precision and speed. Read more »
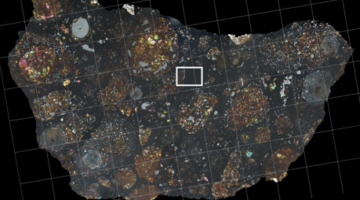
X-Rays Recount Origin of Oddball Meteorites
Reconstructions of 3D patterns of magnetic orientation imprinted in rare meteorites helped resolve questions about their origins. Known as type IIE iron meteorites, they appear to have originated from a parent body that had a composition featuring both fully melted and unmelted parts—other meteorite types display only one composition. Read more »
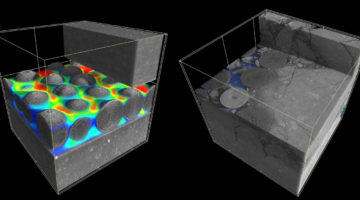
Direct Imaging of Fracture Closure in Reservoir Shales
Using x-ray microtomography at the ALS, researchers identified and characterized the microscale factors affecting fluid flow through shale fractures propped open with sand or ceramic spheres. A better understanding of propped fractures can lead to safer and more efficient recovery of hard-to-reach oil and gas resources. Read more »![]()
![]()
Can Minerals in the Earth’s Lower Mantle Store Water?
Earth is considered a watery planet, simply by virtue of the fact that 71% of its surface is covered by oceans. But researchers have discovered that, in the massive volume of material in Earth’s interior, minerals can serve as an important water reservoir, providing a new perspective on our planet’s water budget. Read more »
Argon: Not So Noble in Earth’s Core
Researchers demonstrated the synthesis of a thermodynamically stable compound of argon and nickel at temperatures and pressures representative of the Earth’s core. The ability of argon, a noble gas, to react with other elements under these conditions may help solve outstanding geological questions, including the “missing argon paradox.” Read more »![]()
A High-Pressure Compound of Argon and Nickel: Noble Gas in the Earth’s Core?
Researchers demonstrated the synthesis of a thermodynamically stable compound of Ar and Ni at thermodynamic conditions representative of the Earth’s core. The results suggest that the abundance of Ar in the Earth’s core is beyond a simple solubility of Ar in molten Ni–Fe but in chemical reactions in nature. Read more »
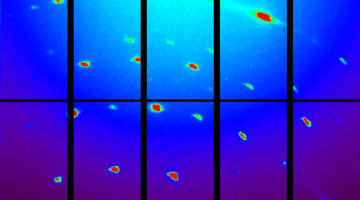
Newly Discovered Minerals Reveal Anomalous Origins
Researchers characterized two highly unusual nickel-containing minerals, both unearthed in an ancient geological site in southern central Siberia. The findings extend our understanding of naturally occurring mineral species and varieties and provide useful insights into the environments leading to the formation of potentially valuable mineral ores. Read more »![]()
![]()
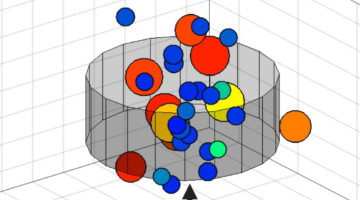
Clues to the Early Solar System Preserved in a Meteorite
Scientists analyzing a tiny carbon-rich pocket inside a meteorite found unexpected chemical signatures. Their findings are the first direct evidence that material from the outer solar system may have traveled inward long before planets formed, providing insight into the early solar system. Read more »