A research team used the ALS to recreate how the Sun breaks apart nitrogen to inform a new model that can be used to understand the fate of a variety of elemental isotopes to explain atmospheric evolution on planets across the solar system. Read more »
ALS Work Using Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an experimental technique used for identifying molecules. Neutral molecules are ionized, and the charged species are sorted by magnetic and/or electric fields according to mass. A mass spectrum is a plot of the ion signal intensity as a function of mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). The atoms or molecules in a sample can be identified by correlating the mass spectrum with known molecular masses or characteristic fragmentation patterns.
Excited States in CO2 Clusters Shed Light on Astrochemical Formation Mechanisms
A vacuum ultraviolet photoionization study conducted at the ALS revealed a new mechanism between molecules that converts high-energy ultraviolet light into free electrons. The results provide insights into interactions between CO2 and organic molecules, which are crucial for understanding astrochemical interactions as well as green chemistry and renewable energy development. Read more »
Electronic energy transfer ionization in naphthalene–CO2 clusters reveals excited states of dry ice
The interaction between CO2 and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is of interest in astrochemically relevant ices, the transition to renewable energy, and the development of green chemistry. We investigate the VUV excitation of the naphthalene–CO2 complex and observe excited states of CO2 through a newly identified electronic energy transfer ionization mechanism. Read more »
Comparative Pore Structure and Dynamics for Bacterial Microcompartment Shell Protein Assemblies in Sheets or Shells
Bacterial microcompartment proteins can assemble into multiple structures, such as sheets, shells, and intermediates. While this is shown artistically in this figure, we study the differences in the pore dynamics within bacterial microcompartment assemblies to assess potential changes in permeability. Read more »
Tracking the reaction networks of acetaldehyde oxide and glyoxal oxide Criegee intermediates in the ozone-assisted oxidation reaction of crotonaldehyde
Criegee intermediates (CIs) are an important class of reactive intermediates with strong oxidizing capability, contributing to the oxidation of atmospheric SOx, NOx, and oxygenated organic compounds. In this work, the reaction networks of two CIs with the same carbon number but different functionality, formed in the ozone-assisted oxidation reaction of crotonaldehyde, are investigated. Read more »
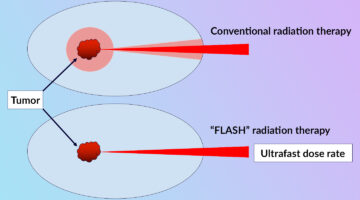
Clarifying the FLASH Effect for Cancer Radiation Therapy
To clarify the underlying mechanisms of the FLASH effect, in which the delivery of ultrafast, high-intensity doses of radiation to tumors counterintuitively reduces damage to surrounding healthy cells, researchers directly compared the oxidative effects of conventional and FLASH techniques using x-ray footprinting at the ALS. Read more »
New Pathway for SO2 Breakup Sheds Light on Earth’s Oxygenation
While calibrating a new scientific apparatus at the ALS, researchers discovered that ultraviolet light can break up sulfur dioxide (SO2) in a new way, with molecular oxygen (O2) as an unexpected product. The discovery sheds light on Earth’s Great Oxygenation Event 2.4 billion years ago, when atmospheric oxygen levels first began to rise. Read more »
The Identity and Chemistry of C7H7 Radicals Observed during Soot Formation
Recent work suggests that resonance-stabilized radicals may participate in chain reactions that lead to soot-particle formation, but their identities and chemistry are poorly understood. C7H7 is often observed in aerosol mass spectra and is generally assumed to be benzyl, the most thermodynamically stable C7H7 isomer. It has now been shown that the identities of these isomers are far more varied, and their chemistry is far more complex, than previously appreciated. Read more »
SO2 Photodissociation at 193 nm Directly Forms S(3P) + O2(3Σg–): Implications for the Archean Atmosphere on Earth
Sulfur isotope patterns in ancient rock layers inform our understanding of Earth’s Archean atmosphere. Before the Great Oxygenation Event (~2.4 billion years ago), hard ultraviolet light penetrated into the Earth’s surface, photodissociating sulfur dioxide directly to S + O2. This new product channel may help resolve discrepancies in the Earth’s evolutionary history. Read more »
Gas-phase synthesis of racemic helicenes and their potential role in the enantiomeric enrichment of sugars and amino acids in meteorites
Molecular-beam experiments with isomer-selective photoionization via a targeted, vinylacetylene-mediated gas-phase reaction of aromatic helicenyl radicals coupled with electronic structure calculations and astrochemical modeling reveal an elegant synthetic route to racemic helicenes – ortho-fused polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), in which benzene building blocks form helically-shaped molecules. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next Page »