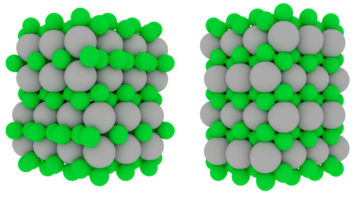
Superhard materials such as metal borides are in demand as structural and engineering compounds and for next-generation cutting tools. Researchers have now synthesized a “solid solution” of two different metal borides, demonstrating the accuracy of theoretical predictions and opening the door to more targeted tuning of desirable characteristics. Read more »
When Rocket Science Meets X-Ray Science
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and NASA are using x-rays to explore, via 3D visualizations, how the microscopic structures of spacecraft heat shield and parachute materials survive extreme temperatures and pressures, including simulated atmospheric entry conditions on Mars. Read more »
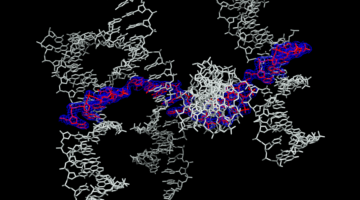
Self-Assembly of a Programmable DNA Lattice
The use of DNA for nanotechnology has gained interest because it is a highly “programmable” polymer with “sticky ends,” allowing the self-assembly of molecular scaffolds for other proteins and molecules. Their high-resolution structures will help map new routes toward the rational design of self-assembling 3D DNA crystals. Read more »
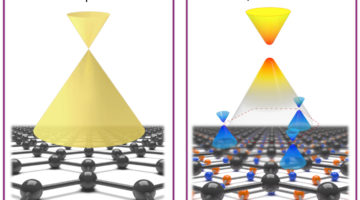
Altered States in Graphene Heterostructures
ARPES directly reveals for the first time how electronic states are altered when epitaxial graphene is deposited on a substrate of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). The interaction between the materials in this heterostructure greatly improves its suitability for advanced, ultralow-power device applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Magnetism Emerges at Wonky Interfaces
Researchers have found a new way to control magnetism at the atomic level that will serve as a model for studying emergent phenomena in other systems. The ability to engineer and tune properties on such small length scales can (eventually) enable us to design exciting new magnetic devices. Read more »
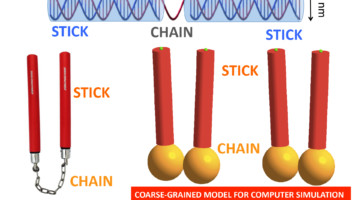
The Smectic Phase of DNA “Nano-Nunchaku”
Researchers designed DNA sequences that self-assemble into a nanoparticle about 50 nm long, composed of two double-stranded DNA duplexes linked together by a single-stranded DNA filament. The nanoparticle resembles nunchaku—a traditional weapon of several martial arts—but 30 million times smaller. Read more »
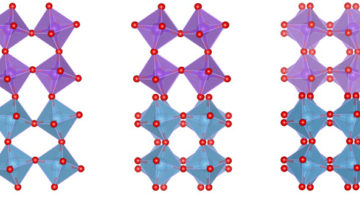
New Multiferroic Material for Ultralow-Power Electronics
Scientists paired ferroelectric and ferrimagnetic materials so that their alignment can be controlled with a small electric field at near room temperatures, a major step in the development of ultralow-power microprocessors, storage devices, and next-generation electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
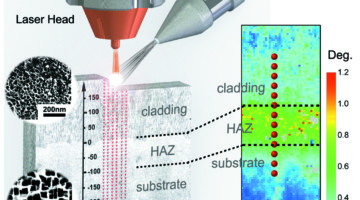
X-Rays Help Evaluate Quality of 3D-Printed Repairs
Laser 3D printing is a promising way to repair machine parts (such as jet-engine turbine blades) made of single-crystal superalloys. But microstructural inhomogeneities created by the high-power laser are a major reliability concern, so researchers employed x-ray Laue microdiffraction to probe the microstructure. Read more »
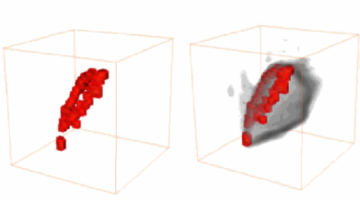
3D Visualization of the Behavior of Grease Additives
Lubricants help keep civilization running smoothly, but is there room for improvement? With the goal of increasing the life span and lowering the costs of all kinds of mechanical and biological systems, researchers used x-ray microtomography to visualize the behavior of grease additives under working conditions. Read more »
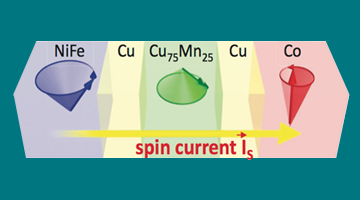
How to Directly Probe ac Spin Currents
Scientists working at the ALS have made the first unambiguous, direct measurements of ac spin currents flowing through nanostructured metal layers. The work represents a crucial step toward the development of future spintronic devices that are smaller, faster, and more energy efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- …
- 26
- Next Page »