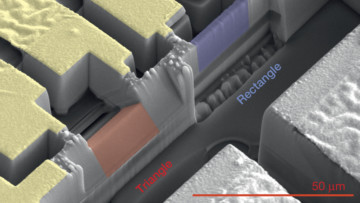
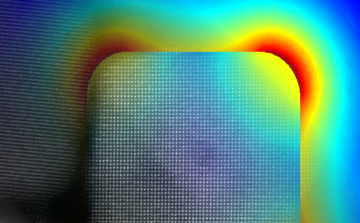
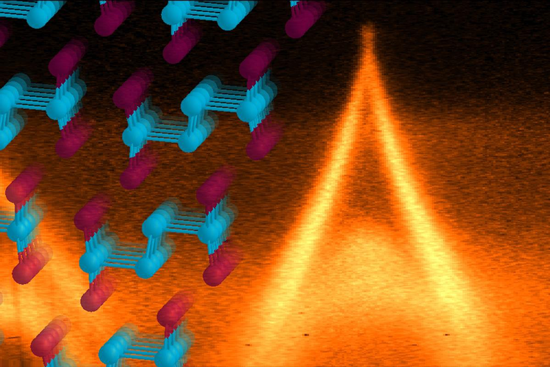
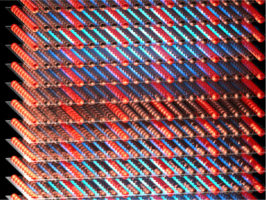
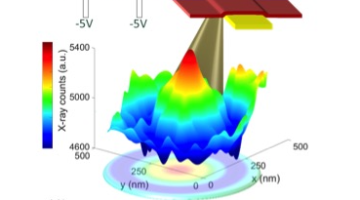
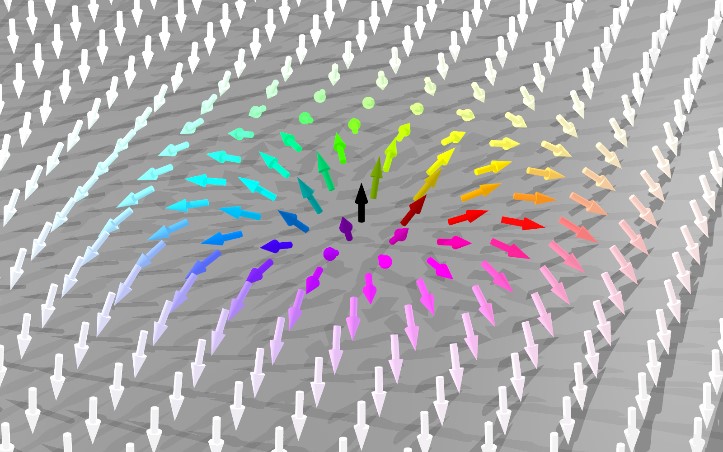
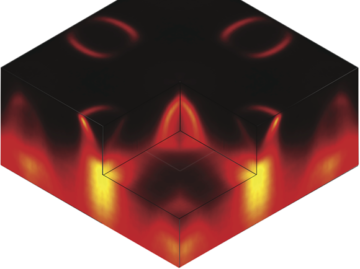
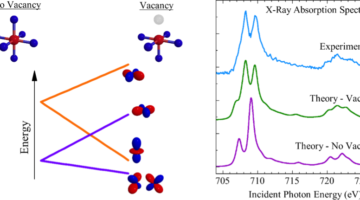
Researchers have observed, for the first time, an exotic 3-D racetrack for electrons in ultrathin slices of a tiny crystal they made at Berkeley Lab. Read more »
A Conscious Coupling of Magnetic and Electric Materials
Scientists have successfully paired ferroelectric and ferrimagnetic materials so that their alignment can be controlled with a small electric field at near room temperatures, an achievement that could open doors to ultralow-power microprocessors, storage devices and next-generation electronics. Read more »
Improving Alloy Memory by Tuning Material Composition
Shape memory alloys can “remember” their original form and return to it repeatedly when heated. To gain structural insight into a new alloy capable of sustaining millions of cycles without failure, researchers performed x-ray Laue microdiffraction at ALS Beamline 12.3.2. Read more »
SINS Reveals Dopant Effects in Plasmonic Materials
Using synchrotron infrared nanospectroscopy (SINS) at the ALS, researchers have for the first time probed infrared plasmonic excitations in single nanocrystals. This allowed the pinpointing of dopant effects on an emerging class of materials with potential for molecular-sensing and energy-harvesting applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Novel Quasi-1D Topological Insulator
The tantalizing prospect of energy-saving, ultralow-power electronics has led to a vigorous search for optimal topological insulator materials. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered the first of a new class of topological insulators with unique properties: quasi-1D bismuth iodide. Read more »
3D Charge Order Found in Superconductor
Resonant soft x-ray diffraction studies of a cuprate high-temperature superconductor revealed a 3D, long-range charge order—the first of its kind ever reported in a cuprate—that competes with superconductivity. A better understanding of such phenomena could help in the design of more robust superconductors with higher transition temperatures. Read more »![]()
![]()
Hewlett Packard Labs Gains Insights with Innovative ALS Research Tools
For the past eight years, Hewlett Packard Labs, the central research organization of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, has been using cutting-edge ALS techniques to advance some of their most promising technological research, including vanadium dioxide phase transitions and atomic movement during memristor operation. Read more »![]()
Driving Skyrmions Along a Racetrack
Researchers have demonstrated the ability to generate stable skyrmion lattices and to drive trains of individual skyrmions by short current pulses along a magnetic racetrack at speeds exceeding 100 m/s, as required for spintronic applications. Read more »
A New Universal Parameter for Superconductivity
Scientists have been researching high-temperature (high-Tc) superconductors for decades with the goal of finding materials that express superconducting capabilities at room temperature, which would be a requirement for practical and cost-effective applications. The newest materials to gain scientific interest are iron-based superconductors, and the latest research from the ALS on these materials indicates a new factor that determines their superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Missing Oxygen Atoms Are Key to Robust Spintronic Material
Researchers studied In2O3:Fe, a promising spintronic material, to determine what leads to its surprisingly robust magnetic properties, how to optimize it, and what to look for in other candidate spintronics materials. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- …
- 26
- Next Page »