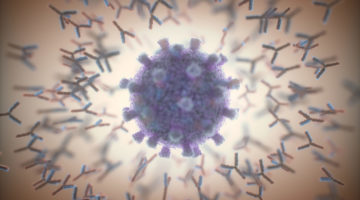
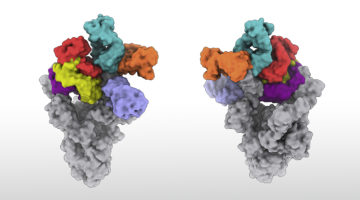
An antibody therapy that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains—including newly emerged mutants that can now “escape” from previous antibody therapies—was developed with a little help from structural biologist Jay Nix. His work helped generate detailed structural maps of how antibodies bind to the spike protein, enabling the selection of promising contenders. Read more »
Guiding Target Selection for COVID-19 Antibody Therapeutics
Protein-structure studies helped demonstrate that the primary target of antibody-based COVID-19 immunity is the part of the virus’s spike protein that can most easily mutate. The work anticipated the rise of SARS-CoV-2 variants and guides the selection of antibody therapeutics that are likely to be more resistant to immune escape. Read more »![]()
![]()
Staff at Berkeley Lab’s X-Ray Facility Mobilize to Support COVID-19-Related Research
X-rays allow researchers to map out the 3D structure of proteins relevant to diseases at the scale of molecules and atoms, and the ALS has been recalled to action to support research related to COVID-19, the coronavirus disease that has already infected about 2 million people around the world. Read more »
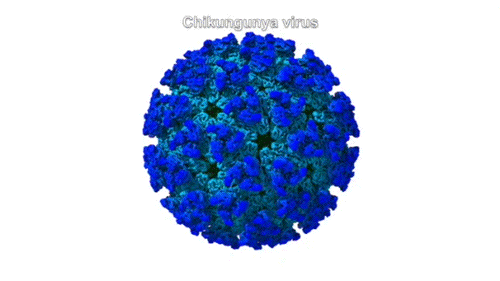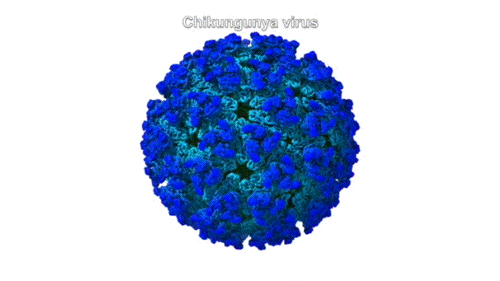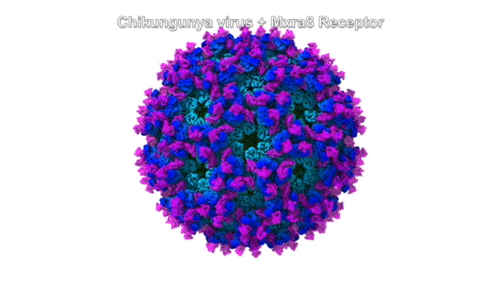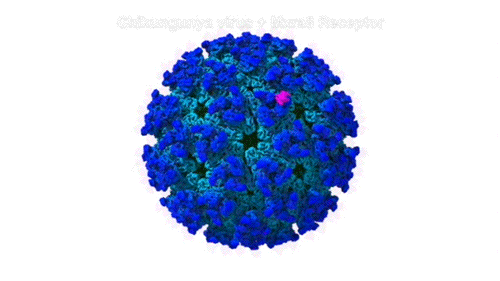
Molecular Handle Enables Viral Attack on Joint Cells
A collaboration of university and industry researchers used x-ray crystallography to investigate how the chikungunya virus, which can cause debilitating joint pain, engages a receptor protein found on the surfaces of joint cells. The work provides a path forward in the fight against a family of viruses that can result in acute and chronic arthritis. Read more »![]()
![]()
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »