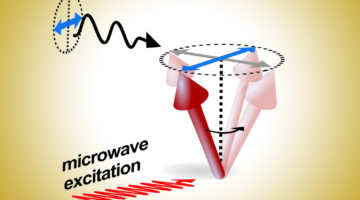
Researchers developed a technique that enables time-resolved, direct detection of spin currents in either ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic materials at GHz frequencies. Studying the dynamic properties of antiferromagnetic spintronic effects could lead to greater stability and faster intrinsic switching speeds compared to conventional spintronics. Read more »
2D MXene Shows Evidence of a Magnetic Transition
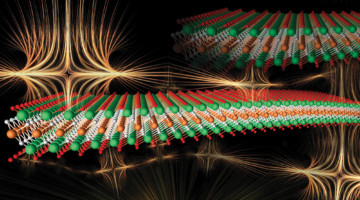
A variety of experiments, including ALS x-ray studies, provided direct evidence of a magnetic transition in a 2D compound called a MXene (pronounced “maxene”). The finding adds new functionality to a family of materials with numerous ways to fine-tune properties for applications ranging from spintronic devices to electromagnetic shielding. Read more »![]()
![]()
Evidence of a magnetic transition in atomically thin Cr2TiC2Tx MXene
2D magnetic materials have recently attracted significant interest as model systems to understand low-dimensional magnetism and for potential spintronic applications. Here, we report on synthesis of Cr2TiC2Tx MXene and a detailed study of its magnetic as well as electronic properties. Read more »
Antiferromagnet Transmits Coherent Spin Waves
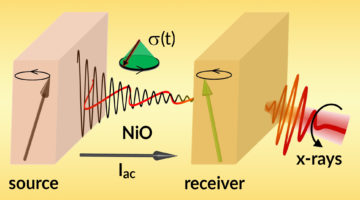
Researchers discovered how pure spin currents (also known as spin waves) can be efficiently and coherently transmitted through an electrically insulating antiferromagnetic material. The work represents a notable milestone in the use of antiferromagnetic materials for low-power spintronic devices at room temperature. Read more »![]()
![]()
Antiferromagnetic Spins Do The Twist
At ALS Beamline 4.0.2, researchers have found that the spins in an antiferromagnetic nanolayer perform a version of “The Twist,” turning one way and then the other, challenging a model that has been a cornerstone of exchange-bias theory for 27 years.
Read more »