-
-
-
- Catalyst chemistry could turn emissions into green fuels
- To become brighter, synchrotron light sources must first go dark
- A pectin-synthesizing enzyme may help trees weather storms. Could it be key to more sustainable bioproducts?
- Strings of magnetic energy shown to flex, wiggle, and reconnect
- The National Academy of Sciences elects two Berkeley Lab researchers
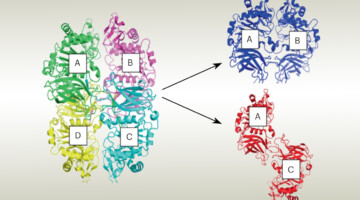
- Researchers capture elusive missing step in the final act of photosynthesis
-
-
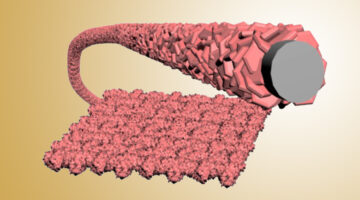
Plant Enzyme Builds Polymers That Fortify Cell Walls
With data obtained at the ALS, researchers gained insight into how an enzyme orchestrates the synthesis of a pectin polymer that imparts strength and flexibility to plant cell walls. The work could lead to improved biofuel production and guide the design of polymers with tailored functionalities for industrial or biomedical applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
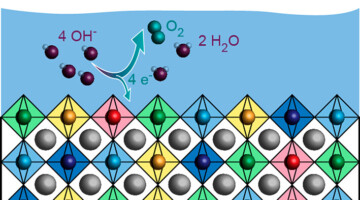
Synergistic Effect Could Boost Production of Green Hydrogen
Researchers developed a composite material of earth-abundant elements that catalyzes the production of green hydrogen much more effectively than similar homogeneous compounds. The composite could potentially be used for efficient hydrogen generation without the need for rare and precious metals like platinum. Read more »
Impact of Thermal Stress on Device Physics and Morphology in Organic Photodetectors
Implementing organic photodetectors (OPDs) into Si-based manufacturing process requires high thermal resistance. This work showcases a comprehensive picture of the impact of high thermal stress (at 200 °C, up to 2 hours) on photosensing performance, bulk and interfacial morphologies, and device physics. Read more »
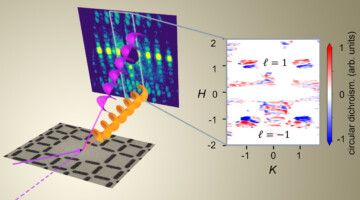
Spiraling Beams Differentiate Antiferromagnetic States
Using spiraling x-ray beams, researchers differentiated between energetically equivalent (“degenerate”) states in an antiferromagnetic lattice. The work shows the potential of these beams to probe properties that would otherwise be inaccessible, to better understand phenomena of fundamental interest and for applications such as spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (April 2023)
-
-
-
- Reinforcement learning: From board games to protein design
- Meet the autonomous lab of the future
- Seven ways Berkeley Lab researchers improve health for all
- Darleane Hoffman and Gabor Somorjai receive the Enrico Fermi Presidential Award
- Autonomous data collection allows focus on analysis rather than acquisition
- Behind the breakthroughs: Anthony Rozales, beamline runner
-
-
Increasing the Energy Density of Hybrid Supercapacitor Electrodes
Hybrid supercapacitors (HSCs) integrate the merits of batteries with those of supercapacitors. However, the fraction of active material in HSC electrodes has remained too low for commercial requirements. Now, researchers have found a clever way to increase the active-mass ratio to achieve dramatic improvements in key measures. Read more »
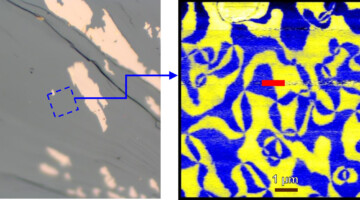
Probing Walls between Electrically Polarized Domains
Researchers used infrared light to investigate the properties of the domain walls that separate electrically polarized (ferroelectric) regions in a rare-earth ferrite material. An understanding of domain-wall behavior is relevant to the development of advanced logic and memory applications for ultralow-power digital devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
Vertical Gradient of Size-Resolved Aerosol Compositions over the Arctic Reveals Cloud Processed Aerosol in-Cloud and above Cloud
Vertical distribution of size-resolved chemical composition of Arctic aerosol particles was investigated in different cloud layers. Multimodal microspectroscopy analysis reveals a broadening of chemically-specific size distribution above the cloud top. Read more »
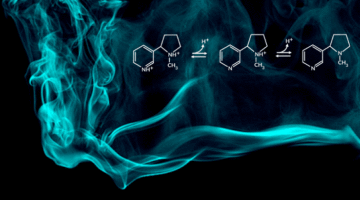
Nicotine Protonation in Simulated Vaping Aerosols
To better understand how e-cigarette additives alter nicotine chemistry and users’ perceptions of vaping, researchers used x-ray spectroscopy technology at the Advanced Light Source to analyze the acid-base equilibria of additive-enhanced nicotine in simulated vaping aerosols. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- …
- 83
- Next Page »