We report, for the first time, sub-4 nm mapping of donor : acceptor nanoparticle composition in eco-friendly colloidal dispersions for organic electronics. This technology shows great promise for the optimization of organic semiconductor blends for organic electronics and photocatalysis and has further applications in organic core–shell nanomedicines. Read more »
The Identity and Chemistry of C7H7 Radicals Observed during Soot Formation
Recent work suggests that resonance-stabilized radicals may participate in chain reactions that lead to soot-particle formation, but their identities and chemistry are poorly understood. C7H7 is often observed in aerosol mass spectra and is generally assumed to be benzyl, the most thermodynamically stable C7H7 isomer. It has now been shown that the identities of these isomers are far more varied, and their chemistry is far more complex, than previously appreciated. Read more »
SO2 Photodissociation at 193 nm Directly Forms S(3P) + O2(3Σg–): Implications for the Archean Atmosphere on Earth
Sulfur isotope patterns in ancient rock layers inform our understanding of Earth’s Archean atmosphere. Before the Great Oxygenation Event (~2.4 billion years ago), hard ultraviolet light penetrated into the Earth’s surface, photodissociating sulfur dioxide directly to S + O2. This new product channel may help resolve discrepancies in the Earth’s evolutionary history. Read more »
Raman and Far-Infrared Synchrotron Nanospectroscopy of Layered Crystalline Talc: Vibrational Properties, Interlayer Coupling, and Symmetry Crossover
Talc is an electrical insulator and an excellent target for low-cost, heterostructure-based optoelectronic applications. Here, light-matter interactions and their consequences at the nanoscale-thickness limit are probed using Raman spectroscopy, near-field synchrotron infrared nanospectroscopy, and first-principles calculations. Read more »
Extreme Closeup of Copper Electrocatalysts in Action
Researchers at Berkeley Lab have made real-time movies of copper nanoparticles as they evolve to convert carbon dioxide and water into renewable fuels and chemicals. Their new insights could help advance the next generation of solar fuels. Read more »
Gemini Beamline 2.0.1 Banks Its First Protein Structure
A protein structure obtained from ALS Beamline 2.0.1 (“Gemini”) has recently been published in the literature and deposited into the Protein Data Bank (PDB)—two significant firsts for this beamline. The structure helped provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in triggering certain inflammatory diseases. Read more »
ALS in the News (March 2023)
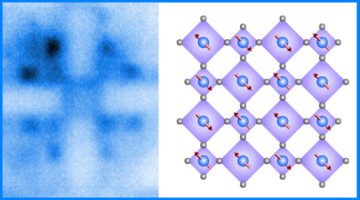
Doped Nickelate Enters a New Phase with Spintronics Potential
Rare-earth nickelates are known to undergo a metal-to-insulator phase transition as temperature decreases, the mechanism of which is not well understood. Here, researchers observed a new low-temperature phase that’s both metallic and antiferromagnetic—an unusual combination with potential value in spintronics. Read more »
Dimitri Argyriou Named Next ALS Director
Dimitri Argyriou, an accomplished physicist and Associate Director for In-Kind Management at the European Spallation Source, has been selected to serve as the next director of the Advanced Light Source. His appointment is expected to begin this June. The announcement follows an international search. Read more »
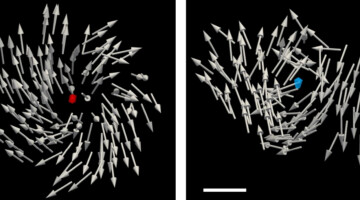
Imaging Topological Magnetic Monopoles in 3D
Researchers created topologically stable magnetic monopoles and imaged them in 3D with unprecedented spatial resolution using a technique developed at the ALS. The work enables the study of magnetic monopole behavior for both fundamental interest and potential use in information storage and transport applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- …
- 83
- Next Page »