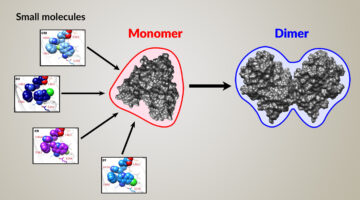
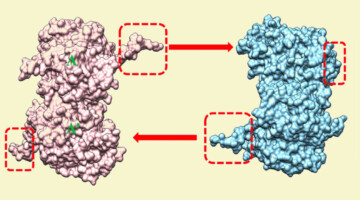
Comparative Pore Structure and Dynamics for Bacterial Microcompartment Shell Protein Assemblies in Sheets or Shells
Bacterial microcompartment proteins can assemble into multiple structures, such as sheets, shells, and intermediates. While this is shown artistically in this figure, we study the differences in the pore dynamics within bacterial microcompartment assemblies to assess potential changes in permeability. Read more »
Caught in the Actinium
In this work, researchers demonstrated a macromolecular scaffold that combines an 8-coordinate synthetic ligand and a mammalian protein to characterize the solution and solid-state behavior of the longest-lived actinium isotope. The information could help design better cancer treatments. Read more »
Tracking the reaction networks of acetaldehyde oxide and glyoxal oxide Criegee intermediates in the ozone-assisted oxidation reaction of crotonaldehyde
Criegee intermediates (CIs) are an important class of reactive intermediates with strong oxidizing capability, contributing to the oxidation of atmospheric SOx, NOx, and oxygenated organic compounds. In this work, the reaction networks of two CIs with the same carbon number but different functionality, formed in the ozone-assisted oxidation reaction of crotonaldehyde, are investigated. Read more »
Engineered π⋯π interactions favour supramolecular dimers X@[FeL3]2(X = Cl, Br, I): solid state and solution structure
Intermolecular interactions drive the formation of biological supramolecular architectures, inspiring the design of artificial supramolecular assemblies and molecular machines. Here, the engineering of supramolecular interactions allows selection of a self-recognition process of dimerization over one of helicate-cage formation. Read more »
Double-Helical Tiled Chain Structure of the Twist-Bend Liquid Crystal Phase in CB7CB
The structure of the twist-bend (TB) phase of the bent dimer CB7CB and its mixtures with 5CB is characterized, revealing a hidden invariance of the self-assembly of the TB structure. Remarkably, the distance along the length for a single turn of this helix is given by 2πRmol, where Rmol is the radius of the bend curvature of a single all-trans CB7CB molecule. Read more »
ALS in the News (June 2024)
-
-
-
-
-
- With x-ray analysis, an asteroid provides a view into our solar system’s past
- Getting up close and personal with…rocks?
- Scientists squeezed infrared light down to 10% of its wavelength. That’s simply incredible.
- Metal alloys that can take the heat
- University of Manchester scientists win prestigious Royal Society of Chemistry Prizes
- Reichel, Shapoval participate in Oakland Unified School District STEM fair
-
-
-
-
Time-Resolved SAXS Screen of Small-Molecule Drug Candidates
Time-resolved, high-throughput, small-angle x-ray scattering improved the screening of small-molecule drug candidates, providing insight into how they stimulate structural transitions in protein targets. The work will speed the discovery of treatments designed to activate biomolecular dynamics associated with desired therapeutic outcomes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Mechanistic Insight into a Viral-Factory Component
Recent protein-structure studies conducted at the ALS provided mechanistic insights into the function of a protein (σNS) involved in viral replication. Understanding these mechanisms will foster the development of therapeutic strategies against viruses that use σNS-like proteins to replicate. Read more »
Revealing unprecedented cathode interface behavior in all-solid-state batteries with oxychloride solid electrolytes
This research provides crucial insights into the innovative design of high-performance all-solid-state batteries (ASSLBs) based on the promising lithium tantalum oxychloride (LTOC) solid electrolytes. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 83
- Next Page »