Realizing over 10% efficiency in printed organic solar cells via scalable materials and less toxic solvents remains a grand challenge. In this article, Harald Ade and co‐workers report chlorine‐free, in‐air blade‐coating of a new photoactive combination, FTAZ:IT‐M, which is able to yield an efficiency of nearly 11%, despite a high humidity of ≈50%. Read more »
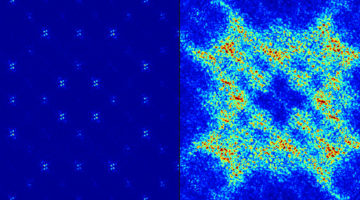
Tuning Magnetic Frustration in a Dipolar Trident Lattice
Researchers designed and fabricated a nanomagnet array in which competing (“frustrated”) magnetic interactions can be directly tuned. Frustrated interactions are key to a wide range of phenomena, from protein folding and magnetic memory to fundamental studies of emergent exotic states. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Microstructure of a Parrotfish Tooth Contributes to Its Toughness
Parrotfish chew on coral, producing hundreds of pounds of sand each year. Mapping the microstructure of parrotfish teeth, scientists found bundles of crystals interwoven like chain mail. The results provide a blueprint for creating ultra-durable materials for mechanical components that undergo repetitive contact, movement, and abrasion. Read more »
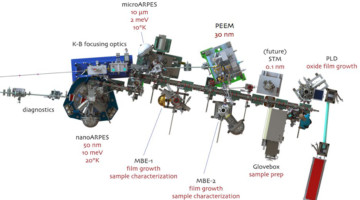
X-Ray Experiments Suggest High Tunability of 2D Material
Using the new MAESTRO platform at the ALS, scientists found that the exotic behavior of electrons in the 2D semiconductor, WS2, may be highly tunable, with possible applications for electronics and other forms of information storage, processing, and transfer. Read more »
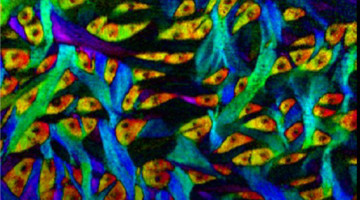
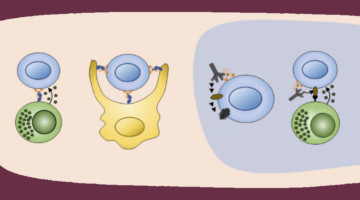
Modified Antibody Clarifies Tumor-Killing Mechanisms
An antibody was modified to activate a specific pathway of the immune system, demonstrating its value in killing tumor cells. The work provides a platform for disentangling different immune-system pathways and could lead to the design of improved immunotherapies. Read more »![]()
![]()
Fuel from the Sun: Insight into Electrode Performance
The mechanisms limiting the performance of hematite electrodes—potentially key components in producing fuel from the sun—have been clarified in interface-specific studies under realistic operating conditions, bringing us a step closer to storing solar energy in chemical fuels. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Path to a Game-Changing Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »![]()
Enhancing the Efficiency of Organic Photovoltaics by a Photoactive Molecular Mediator
In the search for high-efficiency organic solar cells, additives often play an important role in improving the film morphology. Liquid additives, while often effective, evaporate or migrate over time. Herein, Liu et al. report a solid photoactive molecular mediator that could be employed to replace the liquid additives to tune the morphology of bulk heterojunction films for improved device performance. Read more »
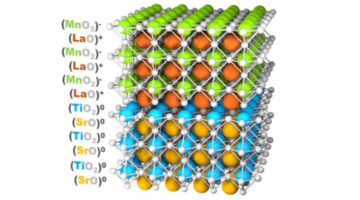
Ferromagnetism Emerges to Alleviate Polar Mismatch
A polar mismatch between nonferromagnetic materials drives an electronic reconstruction in which interfacial ferromagnetism is induced. The emergence of such functionality at interfaces could enable new types of electronics for a range of applications, including logic, memory, sensing, and more. Read more »![]()
X-Rays Provide Key Insights on Path to Lithium-Rich Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- …
- 83
- Next Page »