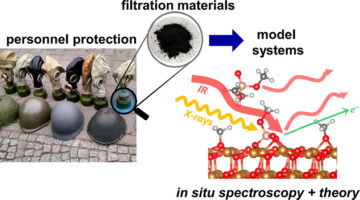
Scientists have put the x-ray spotlight on composite materials in respirators used by the military, police, and first responders. The results provide reassuring news about the effectiveness of current filters and provide fundamental information that could lead to more advanced gas masks as well as protective gear for civilian applications. Read more »
A New Way to Tune Emergent Magnetism
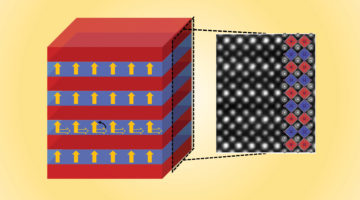
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)—where magnetic moments in a thin film preferentially point out of the plane of the film—is an emergent phenomenon of both fundamental and technological interest. A combination of x-ray techniques demonstrate how to tune PMA in transition-metal oxide multilayers. Read more »![]()
![]()
Revealing the Blue Phase and Other Twisted Orders
Resonant soft x-ray scattering revealed liquid crystal structures that cannot be probed using diffraction, including chiral liquid crystal systems such as the “blue phase” and the twist-bend nematic phase. Information on how individual molecules form functional structures in these systems is key to developing new applications. Read more »
New Catalyst Gives Artificial Photosynthesis a Big Boost
Researchers have created a new catalyst that brings them one step closer to artificial photosynthesis — a system that would use renewable energy to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into stored chemical energy. Read more »
Watching a Quantum Material Lose Its Stripes
In the world of microscopic physics, periodic stripe patterns can be formed by electrons within so-called quantum materials. Scientists have now disentangled the intriguing dynamics of how such atomic-scale stripes melt and form, providing fundamental insights that could be useful in the development of novel energy materials. Read more »
Coral Exoskeleton Growth Begins Inside Living Tissue
Researchers have discovered some good news regarding corals: the mechanism by which their exoskeletons grow may help them resist the effects of ocean acidification. The discovery, made with PEEM studies, has ramifications not only for the health of coral reefs, but for applications such as 3D printing as well. Read more »![]()
![]()
X-Rays Reveal the Biting Truth About Parrotfish Teeth
A parrotfish’s hardy teeth allow it to chomp on coral all day long, ultimately grinding it up through digestion into fine sand. Researchers wanting to see how the fine crystal structure of parrotfish teeth contribute to their incredible strength were able to visualize the orientation of individual crystals, which showed their intricately woven structure. Read more »
Natalie Larson Awarded Neville Smith Student Poster Prize
Natalie Larson, a current ALS doctoral fellow from UC Santa Barbara, won the first prize Neville V. Smith Student Poster Award at the 2017 ALS User Meeting. Larson’s winning poster featured the first two big in situ experiments she performed at Beamline 8.3.2. Read more »
Fuel Cell X-Ray Study Details Effects of Temperature and Moisture on Performance
A specialized type of hydrogen fuel cell requires precise temperature and moisture controls to be at its best. But seeing inside a working fuel cell at the tiny scales relevant to a fuel cell’s chemistry and physics is challenging, so scientists used x-ray-based imaging techniques to study their inner workings. Read more »
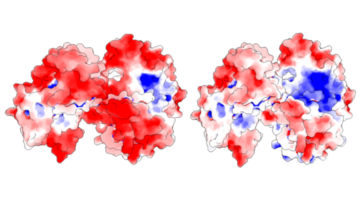
X-Ray Footprinting Solves Mystery of Metal-Breathing Protein
Scientists have discovered the details of an unconventional coupling between a bacterial protein and a mineral that allows the bacterium to breathe when oxygen is not available. The research could lead to innovations in linking proteins to other materials for bioelectronic devices such as sensors that can diagnose disease or detect contaminants. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- …
- 83
- Next Page »