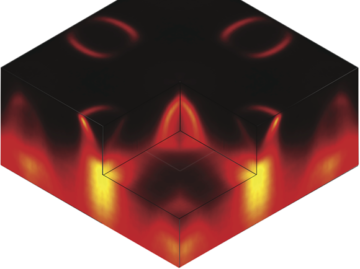
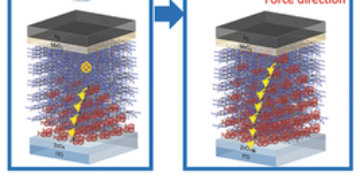
Scientists have been researching high-temperature (high-Tc) superconductors for decades with the goal of finding materials that express superconducting capabilities at room temperature, which would be a requirement for practical and cost-effective applications. The newest materials to gain scientific interest are iron-based superconductors, and the latest research from the ALS on these materials indicates a new factor that determines their superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALSNews Vol. 371
ALSNews Monthly Newsletter of the Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory A New Universal Parameter for Superconductivity Scientists have been researching high-temperature (high-Tc) superconductors for decades with the goal of finding materials that express superconducting capabilities at room temperature, which would be a requirement for practical and cost-effective applications. The newest materials to gainRead More Read more »
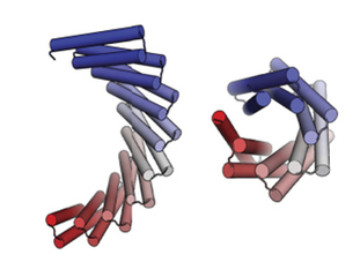
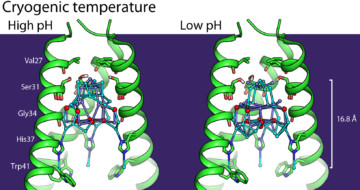
Exploring the Repeat-Protein Universe
Researchers have published a landmark study that used both crystallography and SAXS to validate computationally designed structures of novel proteins with repeated motifs. The results show that the protein-folding universe is far larger than realized, opening up a wide array of new possibilities for biomolecular engineering. Read more »![]()
![]()
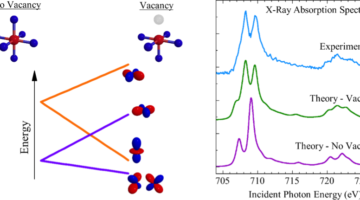
Missing Oxygen Atoms Are Key to Robust Spintronic Material
Researchers studied In2O3:Fe, a promising spintronic material, to determine what leads to its surprisingly robust magnetic properties, how to optimize it, and what to look for in other candidate spintronics materials. Read more »
Superlattices Patterned by Polymers
Scientists have shown that self-assembled superlattices, made up of nanoparticles with polymer chains grafted onto their surfaces (“hairy nanoparticles,” or polymer “brushes”), can be tailored to exhibit desired characteristics for applications ranging from nano- to biotechnology. Read more »
On the Way to Unlimited Energy
With the help of four different ALS beamlines, scientists were able to understand and improve the morphology of the main device structure in organic photovoltaic cells. Read more »![]()
Improving Anti-Influenza Medications
Protein crystallography at ALS Beamline 8.3.1 helped scientists understand the M2 proton-channel structure from the influenza A virus, an understanding that is needed to design better anti-influenza medications. Read more »
ALSNews Vol. 370
ALSNews Monthly Newsletter of the Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Aerosol Oxidation Speeds Up in Smoggy Air To better understand the effects of organic aerosols on climate, pollution, and health, researchers measured aerosol reaction rates at ALS Beamline 9.0.2. They discovered an unexpectedly large acceleration in aerosol oxidation in the presence of anthropogenicRead More Read more »
Aerosol Oxidation Speeds Up in Smoggy Air
To better understand the effects of organic aerosols on climate, pollution, and health, researchers measured aerosol reaction rates at ALS Beamline 9.0.2. They discovered an unexpectedly large acceleration in aerosol oxidation in the presence of anthropogenic pollutants commonly found in smoggy air, a result that could help bring models closer in line with observations. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALSNews Vol. 369
ALSNews Monthly Newsletter of the Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory ALS Director’s Update: Reflections on Our Past, Present, and Future We entered the new year on a very positive note with the passage of a federal budget for fiscal year 2016 that will provide a modest increase in funding for ALS operations. OurRead More Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- …
- 83
- Next Page »