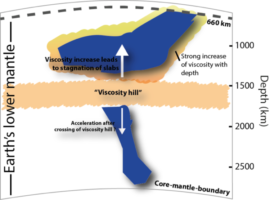
High-pressure experiments at Beamline 12.2.2 on ferropericlase—the presumed weakest mineral found in the Earth’s lower mantle—help explain why subducted slabs of Earth’s crust stall at a depth of around 1000 km (~625 miles). Read more »![]()
All News & Updates
Elaine Chan Fosters ALS/Molecular Foundry Collaboration
In an ongoing effort to build closer working relationships between Berkeley Lab’s light source and nanoscale science research center, Elaine Chan has recently been appointed by the ALS and the Molecular Foundry to a new role as joint ALS/Foundry project scientist. Chan’s mission will be to foster collaborations between the two facility’s users and to communicate a wider understanding about how the two research centers are mutually scientifically beneficial. Read more »
Notification of General User Proposal and Approved Program Results
The Proposal Study Panel (PSP) met April 23–24 to oversee and finalize the scoring of General User Proposals for the 2015-2 operating cycle, and to make recommendations to the ALS Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC) on Approved Program applications. Allocation meetings for each beamline will take place in May. Read more »
2015 ALS Shutdown
The upcoming long-term operating schedule has been published and users will note that it includes an extended shutdown period (October 26, 2015-January 13, 2016) for the ALS. The lengthy shutdown is in part because it spans the Thanksgiving and Holiday shutdown periods, as well as being indicative of the amount of time required to implement major upgrades. The main project for this shutdown is the completion of the final phase of the Storage Ring Radio Frequency (SRRF) Upgrade. Read more »
Peptoid Nanosheets Offer a Diversity of Functionalities
Researchers at the ALS have recently observed peptoid nanosheets as they self-assemble at an oil–water interface. This development opens the door to designing peptoid nanosheets of increasing complexity and functionality for a broad range of applications, including improved chemical sensors and separators, and safer, more effective drug-delivery vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
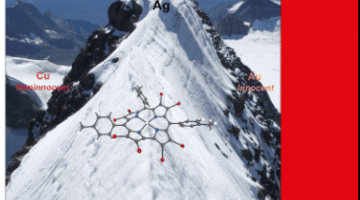
Ligand Noninnocence in Coinage Metal Corroles: A Silver Knife-Edge
In contrast to noninnocent copper corroles and essentially innocent gold corroles, silver corroles appear to be poised on a knife-edge between the two electronic-structural descriptions. The summit trail of Mount Sir Alexander, a peak of the Canadian Rockies described by mountaineer Chris Goulet as a knife-edge that only a mouse can walk on, provides anRead More Read more »
A Milky Mystery: The Case of the Casein Micelles
We all know that milk contains important nutrients such as calcium and protein that help build bones and muscle. But how much do we really know about these ingredients at the molecular level? To learn more, scientists from New Zealand and Australia came to the ALS to x-ray some milk.
Read more »
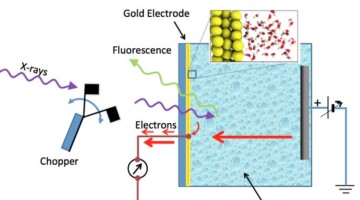
Molecular Structure of Water at Gold Electrodes Revealed
ALS researchers have now made a first-ever observation of the molecular structure of liquid water at a gold surface under different charging conditions. This marks the first time that the scientific community has been able to achieve such high sensitivity in an in situ environment under working electrode conditions. Read more »![]()
![]()
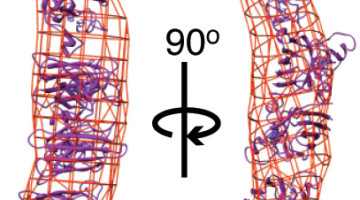
Protein Instability and Lou Gehrig’s Disease
A new study uses small-angle x-ray scattering as well as several advanced biophysical techniques to link protein instability to the progression of a lethal degenerative disease: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
Decoding Ancient Ocean Acidification Signals from Plankton Shells
Ancient plankton shells can record the physical and chemical state of the ocean in which they grew. Decoding these signals can reveal changes in global climate, atmospheric CO2, and the acidity of the oceans in deep geologic time.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- …
- 142
- Next Page »