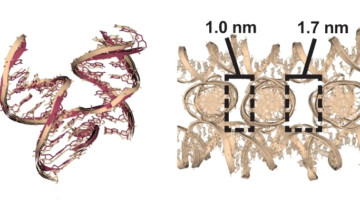
Researchers studied 36 DNA-based molecular junctions and discovered factors that yield superior self-assembled 3D lattice structures. The work expands the set of building blocks for lattices that can scaffold molecules into regular arrays, from proteins for structure studies to nanoparticles for nano-antennas and single-particle sensors. Read more »![]()
![]()
All News & Updates
Protein Structures Aren’t Set in Stone
A group of researchers studying the world’s most abundant protein, an enzyme involved in photosynthesis called rubisco, showed how evolution can lead to a surprising diversity of molecular assemblies that all accomplish the same task. The findings reveal the possibility that many of the proteins we thought we knew actually exist in other, unknown shapes. Read more »
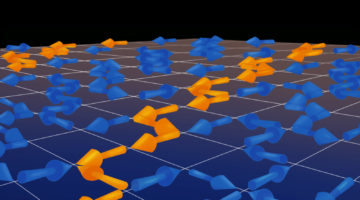
Disorder Drives Long-Range Order in “Tetris Ice” Nanomagnet Arrays
Long-range ordering is typically associated with a decrease in disorder, or entropy. Yet, it can also be driven by increasing entropy in certain special cases. In a recent DOE-funded study, researchers demonstrated that certain artificial spin-ice arrays—nanomagnets lithographically patterned to form Tetris-like shapes—can produce such entropy-driven order. Read more »
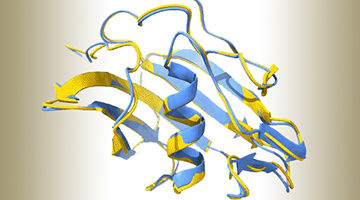
Deep-Learning AI Program Accurately Predicts Key Rotavirus Protein Fold
Rotaviruses are the major causative agents of gastroenteritis worldwide. Attempts to design vaccines are complicated by the rotaviruses’ enormous genetic and immunological diversity. At the ALS, researchers validated the novel structure of a key rotavirus protein, predicted using AlphaFold2, a deep-learning artificial-intelligence program. Read more »
Versatile Sequential Casting Processing for Highly Efficient and Stable Binary Organic Photovoltaics
Ideal bulk heterojunction morphology is critical in organic solar cells (OSCs). Here, researchers show how sequential casting improves device performance in both fullerene- and nonfullerene-based systems, in which the donor and acceptor are deposited sequentially. The film spin-coating method is analogous to the traditional Chinese pancake-making process. Read more »
Ionic Conduction Mechanism and Design of Metal–Organic Framework Based Quasi-Solid-State Electrolytes
This cover image demonstrates the critical role of the solvent in the ion motion of intrinsically anionic metal–organic framework (MOF)–based quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs). Using hybrid theoretical and experimental approaches, we have identified solvent-assisted hopping as the dominant pathway for Li+ conduction in such materials, exemplified by MOF-688. Read more »
Hendrik Ohldag Elected AVS Fellow
Hendrik Ohldag has been elected as a Fellow of the AVS for exploring complex magnetic phenomena using novel x-ray techniques with unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution. Read more »
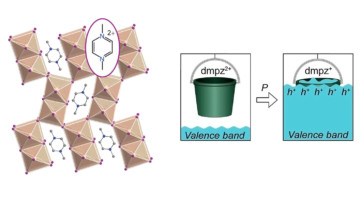
Hybrid Semiconductors Perform Under Pressure
Researchers found that compressing hybrid (organic–inorganic) semiconductors significantly boosts their conductivity. The work demonstrates a novel doping mechanism in which the material’s organic molecules serve as charge reservoirs for tuning charge-carrier concentration, with promising applications in solar cells, lasers, and LEDs. Read more »![]()
![]()
Jinghua Guo to Receive the 2022 Shirley Award
ALS senior scientist Jinghua Guo is the recipient of this year’s Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. Guo is being recognized for pioneering the development of operando soft x-ray spectroscopy, work that’s enabled studies under realistic conditions, which is of great importance in environmental and energy research. Read more »
September 7 Deadline for General User Proposals
The User Office is accepting new General User Proposals (GUPs) from scientists who wish to conduct research at the ALS in the 2023-1 (January–July) cycle. The deadline for submissions is September 7, 2022. Applicants are reminded that they may request joint access to the Molecular Foundry, a nanoscience user facility at Berkeley Lab, to support their ALS activities. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- …
- 139
- Next Page »