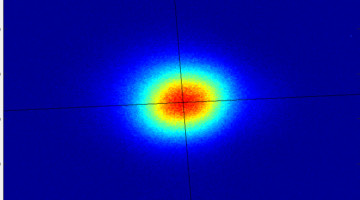
Researchers showed that machine learning can predict noisy fluctuations in the size of beams generated by synchrotron light sources and correct them before they occur. The work solves a decades-old problem and will allow researchers to fully exploit the smaller beams made possible by recent advances in light source technology. Read more »![]()
![]()
All News & Updates
Scientists Explore Egyptian Mummy Bones With X-Rays and Infrared Light to Gain New Insight on Ancient Life
Researchers from Cairo University worked with teams at the ALS to study soil and bone samples dating back 4,000 years. The experiments are casting a new light on Egyptian soil and ancient mummified bone samples that could provide a richer understanding of daily life and environmental conditions thousands of years ago. Read more »
Machine Learning Enhances Light-Beam Performance at the Advanced Light Source
Researchers have successfully demonstrated how machine-learning tools can improve beam-size stability via adjustments that largely cancel out these fluctuations—reducing them from a level of a few percent down to 0.4 percent, with submicron precision. The demonstration shows that the technique could be viable for scientific light sources around the globe. Read more »
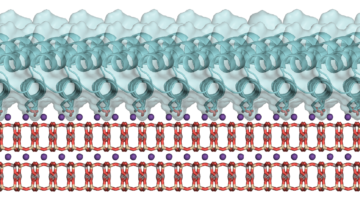
Go With the Flow: Scientists Design Better Batteries for a Renewable Energy Grid
Researchers developed a versatile yet affordable battery membrane—from a class of polymers known as AquaPIMs. This class of polymers makes long-lasting and low-cost grid batteries possible based solely on readily available materials such as zinc, iron, and water. Read more »
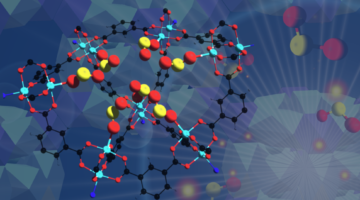
New MOF Can Take On Toxic Sulfur Dioxide Gas
An international team has developed a robust material that can selectively take in toxic sulfur dioxide gas at record concentrations and preserve it for use in chemical production. The researchers verified its performance using a combination of techniques that included x-ray experiments at the ALS. Read more »
Users’ Executive Committee Elections Begin November 4, 2019
Voting for new Users’ Executive Committee (UEC) members will begin on November 4, 2019 and continue through November 18, 2019. We are looking to elect five new members, including one ALS-based member. The newly elected members will take office for a three-year term beginning January 1, 2020. All active users are eligible to go to the UEC website, read about each of the candidates, and submit your votes. The election results will be posted on the site after the deadline. The outgoing committee members are Christine Beavers (Diamond, UK), Jennifer Ciezak-Jenkins (US Army Research Lab), Ethan Crumlin (Advanced Light Source, Berkeley Lab), Kelsey Stoerzinger (Pacific Northwest National Laboratory), and Francesca Toma (Chemical Sciences Division, Berkeley Lab). Read more »
Teamwork Restores ALS Function after PG&E Power Shutoff
In October 2019, Berkeley Lab experienced two PG&E power shutoffs. The efforts of numerous staff across the Lab and at the ALS helped restore function—we walk through the recovery process from earlier this month. Read more »
Dula Parkinson Recognized for Mentorship
At the Mentor Appreciation event on September 6, Berkeley Lab Workforce Development and Education recognized Dula Parkinson for being an Outstanding 2018 STEM Partner. Read more »
Custom-Designed Models Reveal How Proteins Assemble on Minerals
Seashells, bone, and other hard tissues form through a little-understood process combining proteins and minerals. Researchers gained insight using a model system of proteins they designed and synthesized from scratch, characterizing how these building blocks assemble on mica. Read more »
2019 ALS User Meeting Highlights
ALS users and staff gathered to hear the latest news from Washington, the ALS, and each other. The program featured a diverse set of scientific talks and a full slate of workshops and tutorials offering deep dives into topics of interest and, for those new to light sources, introductory presentations designed to demystify the light-source experience. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- …
- 138
- Next Page »