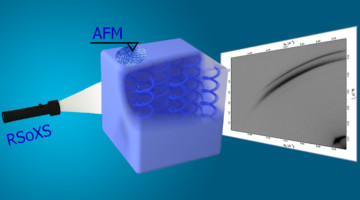
A new, in-beamline spin-coating platform enabled researchers to probe the structure of a promising photovoltaic material in the crucial early stages of processing. The results demonstrate the power of multimodal in situ techniques as promising tools for optimizing synthesis parameters and, thus, device performance. Read more »
Science Briefs
New Catalyst Resists Destructive Carbon Buildup in Electrodes
Key challenges in the transition to sustainable energy can be met by converting CO2 to CO through the use of solid oxide electrolysis cells. But because these can suffer from carbon deposition at the electrodes, researchers have now identified and tested a new, cerium oxide–based catalyst that is more resistant to carbon buildup. Read more »![]()
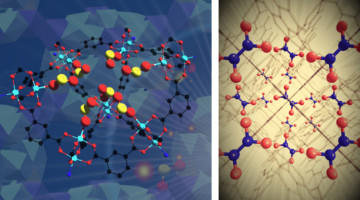
Crystallography Reveals How New Molecular Cages Trap Toxic Gases
Current technologies for reducing toxic gas emissions are often ineffective and wasteful. Crystallographic analyses of two new MOF materials revealed how they reversibly bind their target gases, enabling the materials to be reused over many cycles (reducing waste) and permitting subsequent conversion of the gases into valuable chemical products. Read more »
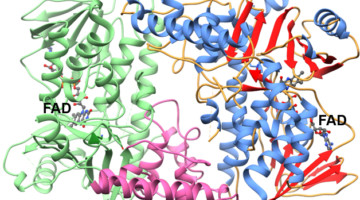
Genetic Blueprint for the Bioproduction of an Antidepressant Drug Candidate
A set of genes from a marine bacterium has been found to encode the biosynthesis of a promising antidepressant drug candidate. This work, which used the ALS to solve the structure of a key enzyme, could enable industrial-scale bioproduction of the drug in ways that are more efficient and sustainable than chemical synthesis. Read more »
Argon: Not So Noble in Earth’s Core
Researchers demonstrated the synthesis of a thermodynamically stable compound of argon and nickel at temperatures and pressures representative of the Earth’s core. The ability of argon, a noble gas, to react with other elements under these conditions may help solve outstanding geological questions, including the “missing argon paradox.” Read more »![]()
Custom-Designed Models Reveal How Proteins Assemble on Minerals
Seashells, bone, and other hard tissues form through a little-understood process combining proteins and minerals. Researchers gained insight using a model system of proteins they designed and synthesized from scratch, characterizing how these building blocks assemble on mica. Read more »
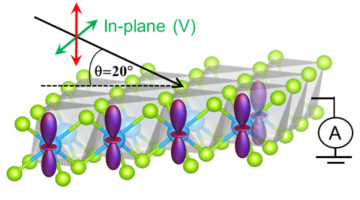
Anomalous Orbital Structure in Two-Dimensional Materials
Researchers explored how structural distortions of the atomic lattice influence exotic electronic states in two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). Polarization-dependent spectroscopy revealed an unexpectedly large crystal-field splitting of the valence electron states, a result of strong hybridization in metal–chalcogen orbitals. Read more »
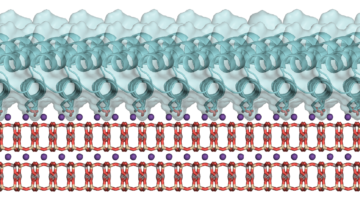
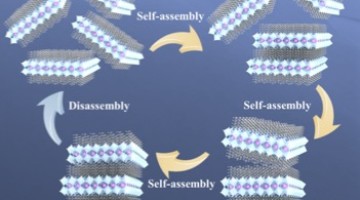
Self-Assembling Nanomaterials Are Organized and Tunable
Perovskite superlattices have a wide variety of applications, but they are difficult to synthesize. Researchers have now characterized their self-assembly process to better understand how to create a variety of superlattice materials. Read more »
Multiple Levels of Chirality from Achiral Molecules
Liquid crystal samples were found to exhibit up to four levels of chirality, despite being made up of achiral molecules. The work sheds light on how molecular properties and competing interactions “propagate” order from the molecular level up to the microscale, leading to complexity similar to that found in biological materials. Read more »
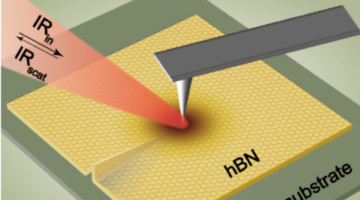
Infrared Nano-Mapping of Local Strain in 2D Materials
Researchers have demonstrated an infrared technique to map and analyze strain in atomically thin crystals of hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) at the nanoscale. This ultrasensitive strain-imaging method could be a promising tool for the examination of low-dimensional materials of interest for electronic and photonic devices. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- …
- 23
- Next Page »