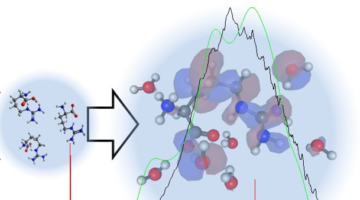
Just 20 amino acids act as building blocks for all our proteins, but their chemical properties have been difficult to study at the most fundamental level. Combining experiments and theory at the ALS, researchers have now determined the ionization energy of arginine, an amino acid with over 100 isomers. Read more »
Science Briefs
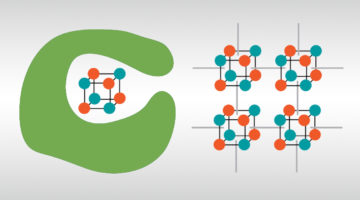
Molecular Framework Imparts Stability to Reactive Catalyst
Researchers have shown that a rigid metal–organic framework (MOF) can be used to stabilize core regions of a reactive catalyst that has potential for use in artificial photosynthesis. The framework immobilizes and preserves key reactive intermediates and affords a clearer view of how the catalyst’s structure correlates with function. Read more »
A Bullfrog’s Powerful Defense Against Toxic Red Tides
Working as a “molecular sponge,” a bullfrog protein known as saxiphilin provides powerful, yet little understood, protection against deadly neurotoxins produced in red tides. Crystallography studies at the ALS have clarified saxiphilin’s function, potentially enabling better ways to monitor and combat toxins in our oceans and food supplies. Read more »![]()
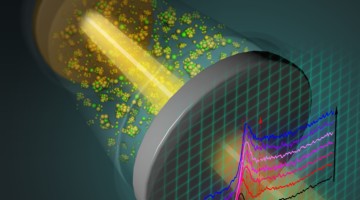
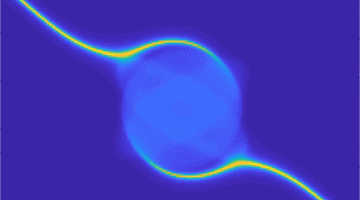
Catalyst Improves Cycling Life of Magnesium/Sulfur Batteries
Magnesium/sulfur batteries hold promise as a safer, energy-dense advancement, but previous iterations have suffered from extremely limited recharging capabilities. Studies at the ALS provided electrochemical insights into battery polarization and revealed how a titanium catalyst activates magnesium/sulfur compounds to improve battery performance. Read more »
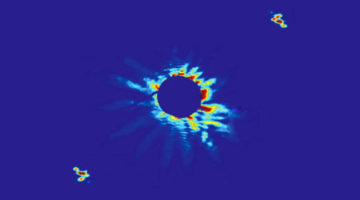
A Crackling Analysis of Stripe and Skyrmion Phases
Through statistical analysis of “crackling” (a system’s jerky response to slowly changing conditions), researchers demonstrated fundamental differences between skyrmion and stripe phases in a layered heterostructure. The method has broad applicability to many complex materials of interest for emerging information technologies. Read more »
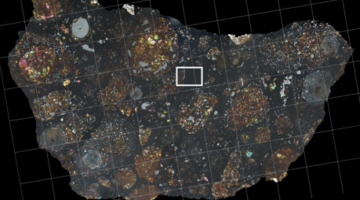
Clues to the Early Solar System Preserved in a Meteorite
Scientists analyzing a tiny carbon-rich pocket inside a meteorite found unexpected chemical signatures. Their findings are the first direct evidence that material from the outer solar system may have traveled inward long before planets formed, providing insight into the early solar system. Read more »
Mirror, Mirror, in the Optimal Spot
Researchers have developed a fast, systematic way to get the best performance out of x-ray mirrors by optimizing their positioning in beamlines. The system does in a day what used to take many days, by combining precise surface metrology with computer analysis of the optimal alignment of a mirror in a beamline. Read more »
Chiral Crystals Give Rise to Topological Conductors
Researchers have discovered materials whose chiral crystal structures produce chirality in their electronic behavior. These topological conductors retain their unique electronic properties regardless of defects and open new possibilities in materials research. Read more »
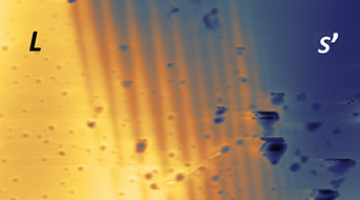
Infrared Light Reveals Microstripes at Insulator-Metal Transition
In this study of a current-driven insulator-to-metal transition, a distinctive stripe pattern develops between the insulating and metallic phases. The work reveals remarkable new features of electrically induced insulator-to-metal transitions in materials with potential applications in energy-efficient memory and transistor devices. Read more »![]()
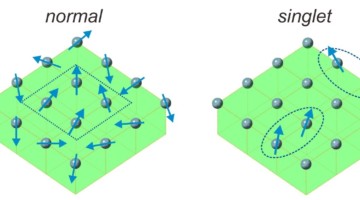
Evidence of a Long-Predicted Magnet
Half a century ago, theorists proposed a novel way for materials to produce a magnetic field. Now, scientists have discovered a uranium compound that bears out that long-ago theory—a new type of magnet that holds promise for enhancing the performance of data storage technologies. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- …
- 23
- Next Page »