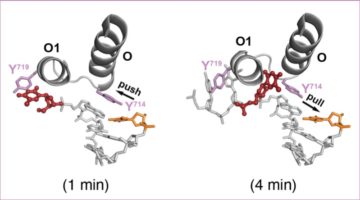
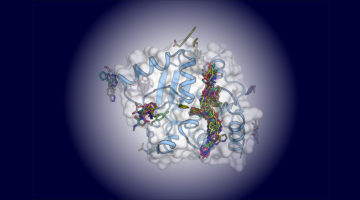
What if the current model for DNA synthesis were flipped on its head? Using time-resolved x-ray crystallography, researchers gained new insights into this essential biological process, revealing that two steps in the synthesis pathway are, in reality, reversed. Read more »
Science Briefs
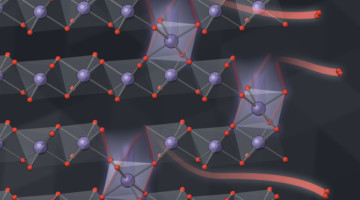
How Iron Remediates Arsenic in Groundwater
Though iron has been demonstrated as an effective means to remediate arsenic contamination in groundwater, the mechanism was not well understood until now. For the first time, researchers have untangled the detailed steps of the interaction, informing more robust strategies for cleanup. Read more »
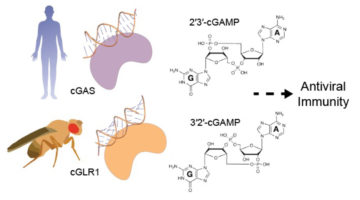
Sounding the Antiviral Alarm: A New Family of Immune-System Sensors
Comparison of enzyme structures from humans and insects revealed a new family of evolutionarily related immune-system sensors, triggered by viral RNA or DNA to produce tailored signals that initiate antiviral action. The results shed new light on the diversity and development of immune defenses in animals. Read more »
The Elusive Electronic Structure of Liquid Metals Unveiled
Over 50 years ago, renowned physicists formulated theoretical models for the electronic structure of liquid metals. Now, for the first time, researchers observed the distinct spectral features predicted by those models, at the interface of a crystalline insulator (black phosphorus) and disordered dopants (alkali metals). Read more »
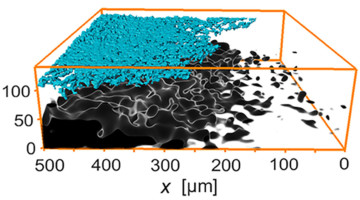
3D View Reveals Shadow Effect after Rapid Battery Charging
Using 3D x-ray microtomography, researchers measured the lithiation levels of particles in Li-ion battery electrodes during charging. At faster charging rates, lithium metal accumulated on the electrode surface and created a “shadow effect,” a region of poor lithiation in the electrode at some distance away from the lithium plating. Read more »
When Timing Isn’t Everything: Spontaneous Chemical Dynamics
Researchers combined aspects of x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with correlation spectroscopy—a statistical method capable of detecting patterns in microscopic fluctuations across space and time. The new technique, called time-correlation XPS, allows researchers to monitor dynamics without the need for a timed trigger. Read more »
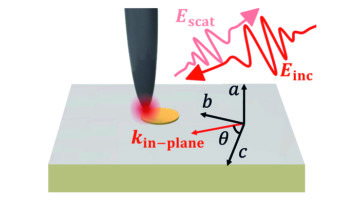
A Powerful Infrared Technique Broadens Its Horizons
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) focuses infrared light to dimensions below the diffraction limit, measuring properties with components perpendicular to the sample surface. Researchers have now devised a way to probe components parallel to the sample, where the technique has been less sensitive. Read more »
Sifting through Fragments for COVID-19 Treatments
COVID-19 vaccines are essential for preventing serious disease, but the identification of new drugs is still necessary for the treatment of patients who become sick as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, scientists used computational docking and crystallography to screen large numbers of small molecules for potential use in drug compounds. Read more »
A Multiscale Picture of Oxygen Loss in Battery Electrodes
In lithium-ion batteries, oxygen atoms leak out of electrode particles as the lithium moves back and forth between electrodes. Now, researchers have measured this process at multiple length scales, showing how the oxygen loss changes the electrode’s structure and chemistry, gradually reducing the amount of energy it can store. Read more »
In a Hawaiian Lava Fountain, Fluid Magma Turns Brittle
Compared to the violent explosions of Mount Vesuvius or Mount St. Helens, Hawaiian volcanic eruptions are relatively calm, characterized by flowing rivers and fountains of lava. Here, researchers have discovered that even low-viscosity magma sometimes behaves more like brittle glass that shatters into fine particles. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 23
- Next Page »