To explore what happens to minerals under the extreme conditions in Earth’s mantle, researchers developed an x-ray technique that bridges the gap between methods that reveal bulk properties and those that focus on individual crystals. Use of the technique has shed light on the dynamics of tectonic-plate subduction in Earth’s lower mantle. Read more »
Science Briefs
Researchers Set Sights on Another COVID-19 Target
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, it was quickly established that the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is a prime target for neutralizing antibodies. Now, scientists have found a second region of the spike protein that is targeted by dozens of antibodies, some of which exhibit ultrapotent neutralizing activity. Read more »
Scientists Uncover a Different Facet of Fuel-Cell Chemistry
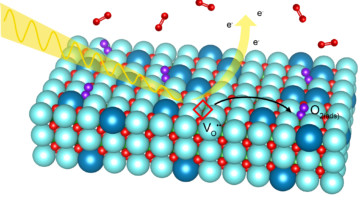
Solid oxide fuel cells are a promising technology for cleanly converting chemical energy to electrical energy. To improve the efficiency of these devices, researchers studied a model electrode material in a new way—by exposing a different facet of its crystal structure to oxygen gas at operating pressures and temperatures. Read more »
New Tools Link Catalytic Activity to Nanoscale Transformations
Transitioning to a clean hydrogen economy will require cheaper, more efficient ways to split water molecules. To address bottlenecks in the water-splitting process, researchers developed a suite of advanced tools, including a liquid flow cell that enables electrochemical studies of catalysts under working conditions. Read more »
Graphene Outperforms Metal Junctions for 2D Semiconductors
Researchers found that graphene performs ten times better than metal in transmitting a photoinduced current across interfaces with 2D semiconductors. Nanoscale-resolution band-structure measurements provided a deeper understanding of charge transport in these systems and will help in engineering more efficient contacts. Read more »
Meteorites Reveal Magnetic Record of Protoplanet Churn
Researchers detected the signatures of ancient magnetic fields imprinted in the ferromagnetic grains of meteorites that originated from the same parent body. The results, combined with radioisotopic dating of the samples, support an extended time frame for the cooling of molten protoplanetary cores. Read more »
Coral Skeleton Reveals Hidden Structures under Multimodal Scrutiny
A powerful new microscope combining ptychography with x-ray linear dichroism provides nanoscale insight into the biomineral strength and resilience of a coral skeleton. The technique’s previously unachievable spatial resolution and contrast will open up new lines of research for users of x-ray microscopy at the ALS. Read more »
Skyrmion Creation and Annihilation Made Simple
Researchers developed a simple approach to writing and deleting skyrmions on demand, using heat and magnetic fields generated by an electrical current, by-products normally considered problematic. The ubiquitous character of these effects, coupled with simplicity of design, offers much-needed scalability and broad applicability. Read more »
To Speed Discovery, Infrared Microscopy Goes “Off the Grid”
Researchers developed a highly efficient way to collect infrared microscopy data that avoids the use of slow, grid-based raster scans. The method substantially reduces image-acquisition times by autonomously increasing sampling density in regions of interest, facilitating infrared spectromicroscopy of biochemical processes in real time. Read more »
Actor in a Supporting Role: Substrate Effects on 2D Layers
ALS studies highlighted interactions that can occur between technologically intriguing 2D materials and the substrates that physically support them. The results provide important insights into the issue of non-negligible interlayer coupling and demonstrate the potential for tuning single-layer properties through substrate engineering. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 23
- Next Page »