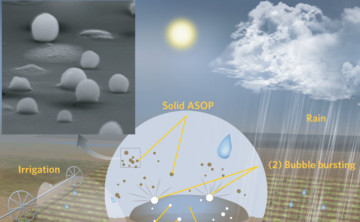
Rain’s reputation for cleansing the air may come with a caveat after new findings, including STXM and NEXAFS data, show that raindrops play a role in generating airborne organic particles. The findings could influence how scientists model our planet’s climate and future. Read more »
ALS Work Using STXM
Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy (STXM) generates microscopic images of a thin section of specimen by raster-scanning it in a focused x-ray beam. The flux of transmitted x-rays is measured to obtain the image intensity. By holding the beam at a microscopic region of interest on the sample while the photon energy is scanned, chemically sensitive x-ray absorption spectra can be measured at that specific location (spectromicroscopy).
Hewlett Packard Labs Gains Insights with Innovative ALS Research Tools
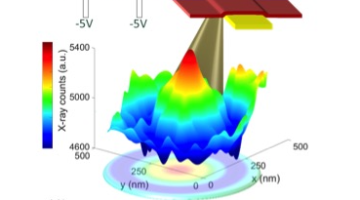
For the past eight years, Hewlett Packard Labs, the central research organization of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, has been using cutting-edge ALS techniques to advance some of their most promising technological research, including vanadium dioxide phase transitions and atomic movement during memristor operation. Read more »![]()
Decoding Ancient Ocean Acidification Signals from Plankton Shells
Ancient plankton shells can record the physical and chemical state of the ocean in which they grew. Decoding these signals can reveal changes in global climate, atmospheric CO2, and the acidity of the oceans in deep geologic time.
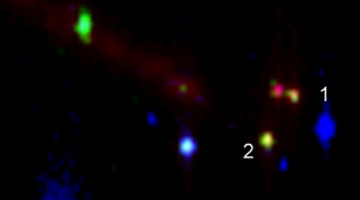
Space Dust Analysis Could Provide Clues to Solar System Origins
New studies of space dust captured by NASA’s Stardust Interstellar Dust Collector have shown that interstellar particles may be much more complex in structure and composition than previously thought. Read more »![]()
![]()
Concrete Industry Benefits from Ancient Romans and the ALS
New insights into the ancient Romans’ ingenious concrete harbor structures emerging from ALS beamline research could move the modern concrete industry toward its goal of a reduced carbon footprint.
Chloride Depletion in Aged Sea Salt Particles
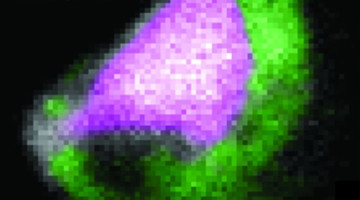
Elemental and chemical imaging analyses showed that sea salt particles react with water-soluble organic acids in the atmosphere through a unique mechanism which had been overlooked in atmospheric chemistry. The reactions release volatile hydrogen chloride into the atmosphere and leave behind sea salt particles drained of chloride.
Read more »
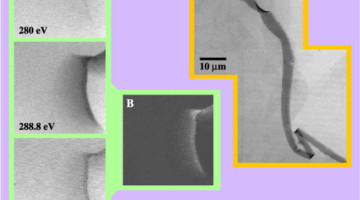
Nanoscale Chemical Imaging of a Working Catalyst
Researchers identified the chemical species present for an iron-based Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalyst and to image their distribution on the nanoscale. When developed further, this new tool may give chemists the ability to design and tailor catalysts for maximum selectivity and efficiency in a wide range of chemical processes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Particles from Comet 81P/Wild 2 Viewed by ALS Microscopes
NASA’s $200-million, seven-year-long Stardust mission returned to Earth thousands of tiny particles snagged from the coma of comet 81P/Wild 2. Four ALS beamlines and the researchers using them were among the hundreds of scientists and dozens of experimental techniques in facilities around the world that contributed to the preliminary examination of the first samples.
Read more »![]()
![]()
Crosslink Density of Superabsorbent Polymers
Researchers from The Dow Chemical Company teamed with academic colleagues to conduct x-ray spectromicroscopy studies of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs), materials with a wide range of applications, including disposable baby diapers. Dow has been able to use the results to help develop the process technology for a new SAP-manufacturing plant. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6