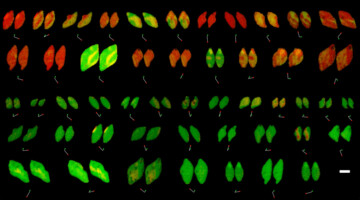
The ability to harness the 4f-orbital anisotropies and magnetic susceptibilities of lanthanide elements is key to their application in molecular magnetism, including as molecular qubits and single-molecule magnets. Here, 4f orbital mixing and its impact on the magnetic susceptibility of a trivalent Eu organometallic complex was analyzed experimentally. Read more »
“Computer Vision” Review of X-Ray Movies Leads to New Insights
Using a type of machine learning called “computer vision” to mine data from x-ray movies, researchers made new discoveries about the reactivity of a material in rechargeable batteries. The results suggest that optimizing the carbon layer thickness on the electrode surface could help researchers to design more efficient batteries. Read more »
Will Chueh to Receive the 2023 Shirley Award
Will Chueh of Stanford University is the 2023 winner of the Shirley award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. His selection recognizes Chueh’s deep contributions in operando soft x-ray spectromicroscopy for imaging electrochemical redox phenomena—images and movies for battery and electrocatalytic reactions. Read more »
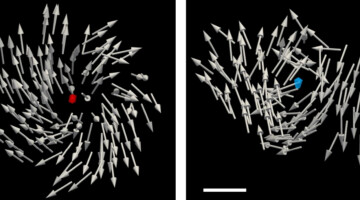
Imaging Topological Magnetic Monopoles in 3D
Researchers created topologically stable magnetic monopoles and imaged them in 3D with unprecedented spatial resolution using a technique developed at the ALS. The work enables the study of magnetic monopole behavior for both fundamental interest and potential use in information storage and transport applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
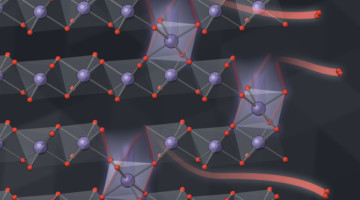
A Multiscale Picture of Oxygen Loss in Battery Electrodes
In lithium-ion batteries, oxygen atoms leak out of electrode particles as the lithium moves back and forth between electrodes. Now, researchers have measured this process at multiple length scales, showing how the oxygen loss changes the electrode’s structure and chemistry, gradually reducing the amount of energy it can store. Read more »
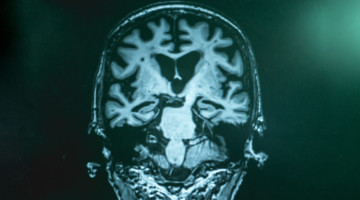
Nanoscale Metallic Particles Detected in Brain Tissue
Researchers detected nanoscale deposits of elemental copper and iron in brain tissues isolated from Alzheimer’s disease subjects. The discovery suggests new directions of study to determine the role that elemental metals might play in neurochemistry, neurobiology, and the development of neurodegenerative disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Tools Link Catalytic Activity to Nanoscale Transformations
Transitioning to a clean hydrogen economy will require cheaper, more efficient ways to split water molecules. To address bottlenecks in the water-splitting process, researchers developed a suite of advanced tools, including a liquid flow cell that enables electrochemical studies of catalysts under working conditions. Read more »
X-Ray Experiments, Machine Learning Could Trim Years Off Battery R&D
Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy at the ALS’s COSMIC beamline contributed to a battery study that used an innovative approach to machine learning to speed up the learning curve about a process that shortens the life of fast-charging lithium batteries. It represents the first time this brand of “scientific machine learning” was applied to battery cycling. Read more »
A Closer Look at Water-Splitting’s Solar Fuel Potential
Although bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is a theoretically attractive material for electrodes in photoelectric chemical cells (PECs) used for artificial photosynthesis, it hasn’t lived up to its potential. Researchers used a multimodal approach to gain new insight into what might be happening at the nanoscale to hold BiVO4 back. Read more »
Salt in the Amazon Air Comes from Local Fungi
The abundant salt in the atmosphere above the Amazon basin has long been attributed to the Atlantic Ocean. But now, using the Advanced Light Source, scientists have found that much of it originates much more locally: fungal spores in the rainforest. Pinpointing the origin will improve climate models and understanding of rainforest ecosystems. Read more »