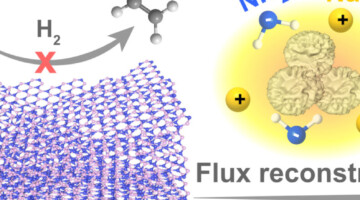
Researchers engineered defects in boron nitride to develop a metal-free route for purifying ethylene to remove acetylene. The ALS shed light on how the engineered defects were responsible for exceptional selectivity. Read more »
Efficient Upcycling of Plastic Waste into Useful Liquid Fuels
Researchers found a way to turn single-use plastics (e.g., grocery bags and packaging) into useful liquid fuels, like components of gasoline or diesel, without needing high heat, rare metals, or added chemicals. The work presents a promising pathway to address the global plastic waste crisis, with both environmental and economic advantages. Read more »
Polyethylene Upcycling to Liquid Alkanes in Molten Salts under Neat and External Hydrogen Source-Free Conditions
Researchers found a way to turn single-use plastics (e.g., grocery bags and packaging) into useful liquid fuels, like components of gasoline or diesel, without needing high heat, rare metals, or added chemicals. The work presents a promising pathway to address the global plastic waste crisis, with both environmental and economic advantages. Read more »
Nanoconfinement of High Hydrogen-to-Metal Ratio Lanthanum Hydrides in Functionalized Carbon Hosts
Metal hydrides with a high hydrogen content are important for materials-based hydrogen storage and high-temperature superconductivity. Nanoconfinement of metal hydrides in porous hosts is a promising strategy to tune the thermodynamic stability and control the hydrogen-to-metal ratio. X-ray absorption and photoelectron spectroscopy provided detailed information about the local chemical environment of LaHx species within carbon hosts. Read more »
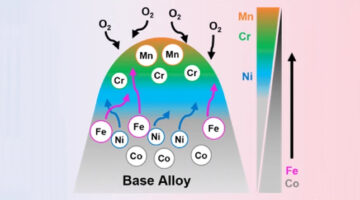
Tracking Oxidation in “High-Entropy” Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements
For extreme applications such as nuclear fusion reactors and high-temperature jet engines, scientists are experimenting with “high-entropy” alloys that consist of many metals mixed together in equal proportions. In this work, researchers begin to unravel how these materials degrade under high-temperature oxidative environments. Read more »![]()
Tuning the Spin Transition and Carrier Type in Rare-Earth Cobaltates via Compositional Complexity
This work demonstrates that tunable disorder in a crystal can be quite useful: compositional site disorder was used to modify oxide semiconductors by changing the carrier type, improving crystallinity and tuning a spin transition. Applications include electrothermal thresholding devices such as radio frequency limiters. Read more »
Revealing unprecedented cathode interface behavior in all-solid-state batteries with oxychloride solid electrolytes
This research provides crucial insights into the innovative design of high-performance all-solid-state batteries (ASSLBs) based on the promising lithium tantalum oxychloride (LTOC) solid electrolytes. Read more »
HyMARC Aims to Hit Targets for Hydrogen Storage Using X-Ray Science
Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
Increasing the Energy Density of Hybrid Supercapacitor Electrodes
Hybrid supercapacitors (HSCs) integrate the merits of batteries with those of supercapacitors. However, the fraction of active material in HSC electrodes has remained too low for commercial requirements. Now, researchers have found a clever way to increase the active-mass ratio to achieve dramatic improvements in key measures. Read more »
Visualizing the Nanoscale Oxygen and Cation Transport Mechanisms during the Early Stages of Oxidation of Fe–Cr–Ni Alloy Using In Situ Atom Probe Tomography
Understanding the early stages of interactions between oxygen and material surfaces is beneficial for fields ranging from materials degradation to forensics and catalysis. In situ atom probe tomography (APT) is demonstrated to track the diffusion of oxygen and metal ions at nanoscale spatial resolution during the early stages of oxidation of a model Fe–Cr–Ni alloy. Read more »