Protein-structure studies performed in part at the ALS helped researchers discover that the protein assemblies in a key carbon-cycling enzyme can rearrange with surprising ease. The findings raise the prospect of genetically tuning the protein in agricultural plant species to produce more productive and resource-efficient crops. Read more »![]()
![]()
Chemical acylation of an acquired serine suppresses oncogenic signaling of K-Ras(G12S)
Small-molecule targeting of particular KRAS mutations offer promise for cancer therapy. The cover depicts a small-molecule ligand (red) inhibiting the oncogenic mutant protein K-Ras(G12S) (cyan) by forming a covalent ester adduct at the mutant serine. Read more »
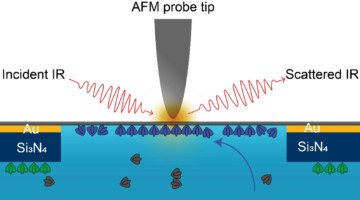
A Nano-IR Probe for Proteins in Liquid Environments
A new technique using infrared (IR) light revealed how the self-assembly of proteins is affected by environmental conditions in a surrounding liquid. This nanoscale probe of soft matter in a liquid matrix will facilitate advances in biology, plastics processing, and energy-relevant applications such as electrocatalysts and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
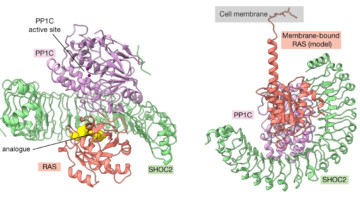
Structures Signal Fresh Targets for Anticancer Drugs
Researchers from Genentech used a suite of methods, including small-angle x-ray scattering, to learn how an assembly of three proteins works together to transmit signals for cell division. The work reveals new targets for the development of drugs that fight certain types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
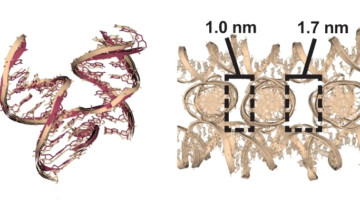
An Expanded Set of DNA Building Blocks for 3D Lattices
Researchers studied 36 DNA-based molecular junctions and discovered factors that yield superior self-assembled 3D lattice structures. The work expands the set of building blocks for lattices that can scaffold molecules into regular arrays, from proteins for structure studies to nanoparticles for nano-antennas and single-particle sensors. Read more »![]()
![]()
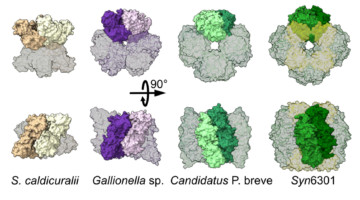
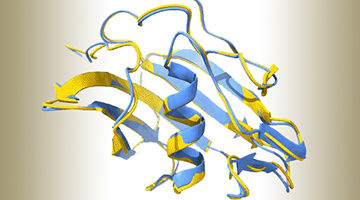
Protein Structures Aren’t Set in Stone
A group of researchers studying the world’s most abundant protein, an enzyme involved in photosynthesis called rubisco, showed how evolution can lead to a surprising diversity of molecular assemblies that all accomplish the same task. The findings reveal the possibility that many of the proteins we thought we knew actually exist in other, unknown shapes. Read more »
Deep-Learning AI Program Accurately Predicts Key Rotavirus Protein Fold
Rotaviruses are the major causative agents of gastroenteritis worldwide. Attempts to design vaccines are complicated by the rotaviruses’ enormous genetic and immunological diversity. At the ALS, researchers validated the novel structure of a key rotavirus protein, predicted using AlphaFold2, a deep-learning artificial-intelligence program. Read more »
Molecular Switch Triggers Changes in Plant Structure
Using x-ray crystallography, biochemistry, and plant genetics, researchers identified a molecular switch that triggers modifications to plant structure in response to environmental conditions. A greater understanding of this adaptive process will help scientists optimize plants for efficient nutrient uptake and resistance to parasitic species. Read more »![]()
![]()
Phosphomimetic S207D Lysyl–tRNA Synthetase Binds HIV-1 5′UTR in an Open Conformation and Increases RNA Dynamics
Binding assays, RNA chemical probing, and SAXS showed that phosphomimetic S207D LysRS binds in an open conformation preferentially to dimeric HIV-1 genomic RNA. A new working model is proposed wherein a dimeric phosphorylated LysRS/tRNA complex binds to a genomic RNA dimer, facilitating tRNA primer release and placement onto the binding site. Future anti-viral strategies that prevent this interaction are envisioned. Read more »
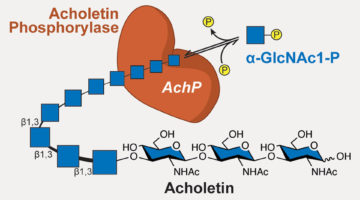
Bacterial Enzyme Produces Biodegradable Polymer
Researchers discovered a bacterial enzyme that synthesizes a biopolymer whose repeating units are linked together in way that had not been previously observed. The new polymer is biodegradable and may be biocompatible, with potential for applications ranging from medical therapeutics to eco-friendly plastic alternatives. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 24
- Next Page »