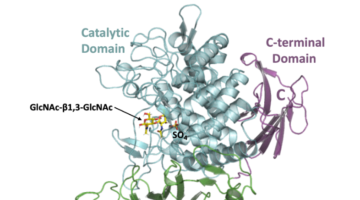
Researchers identified a bacterial enzyme that produces a novel biopolymer. The polymer, dubbed acholetin, is a chain of sugar molecules known as a polysaccharide. Acholetin is similar in structure to chitin, the major component of insect exoskeletons, and holds promise as a useful biomaterial because of its biodegradability and biocompatibility. Read more »
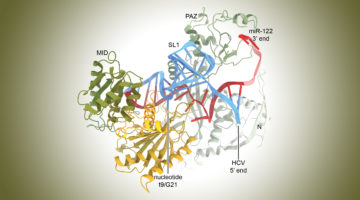
Molecular Hijacking of a MicroRNA by the Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV), which attacks the liver, is known to repurpose host-cell components known as microRNAs—short RNA strands that act to silence gene expression. Now, the molecular structure of an HCV site bound to a microRNA complex revealed how their interactions shield the virus from the host cell’s protective response. Read more »
Biomineralization: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary history
In this review, Gilbert et al. develop a model for calcium carbonate biomineralization applicable to all phyla. Their model may help elucidate the key genetic components that drive biomineralization and offers insight into the consequences of global climate change on marine organisms. Read more »
Loss of biological control of enamel mineralization in amelogenin-phosphorylation-deficient mice
Amelogenin phosphorylation plays crucial roles in controlling structural, crystallographic, mechanical, and compositional characteristics of dental enamel. Thus, loss of amelogenin phosphorylation leads to a reduction in the biological control over the enamel mineralization process. Read more »
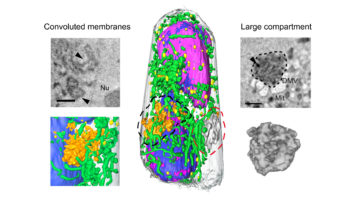
Safely Studying Dangerous Infections Just Got a Lot Easier
Researchers have cranked up the speed of imaging infected cells using soft x-ray tomography, a technique that can generate incredibly detailed, three-dimensional scans. The approach gives an easy way to quickly examine how cells’ internal machinery responds to SARS-CoV-2, or other pathogens, as well as how the cells respond to drugs designed to treat the infection. Read more »
Rapid 3D Visualization of Lung Cells Altered by SARS-CoV-2
In this work, researchers illustrated the potential of soft x-ray tomography to rapidly characterize and quantify the structural changes induced in cells infected by SARS-CoV-2, revealing profound alterations of the subcellular architecture induced by viral infection over time. Read more »
How Shark Egg Cases Balance Toughness and Permeability
Also known as “mermaid’s purses,” shark egg cases are both tough and permeable—two opposing characteristics that are necessary for the embryo’s survival. X-ray scattering at the ALS and electron microscopy helped explain how the material’s nanoarchitecture contributes to its toughness, informing future development of high-performance synthetic materials. Read more »
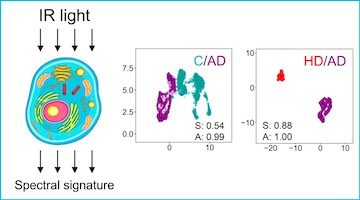
Spectral Phenotyping for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease may soon be within reach, thanks to spectral phenotyping. Using infrared spectroscopy, Berkeley Lab researchers developed this technique to detect the subtle biochemical changes in a “cellular fingerprint” that is characteristic of the devastating disease. Read more »
The three-dimensional construction of leaves is coordinated with water use efficiency in conifers
3D anatomical views of conifer leaves with diverse morphologies, generated using synchrotron microCT imaging (colors show different segmented tissues). Top–bottom: Pinus monticola, P. pungens, and Wollemia nobilis. Image courtesy of Santiago Trueba. Read more »
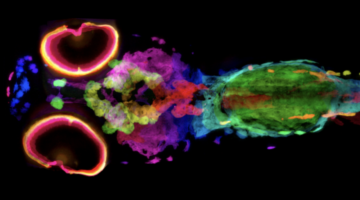
New Technique Visualizes Every Pigment Cell of Zebrafish in 3D
Researchers developed a new technique that uses x-ray microtomography and silver staining to image every pigment cell of a whole zebrafish in 3D. The method could be used to learn more about the 3D architecture of melanoma tumors and potentially guide treatment decisions. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 24
- Next Page »