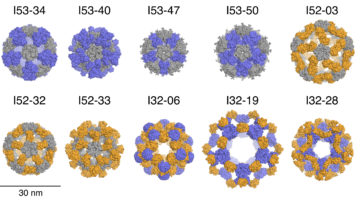
Inspired by protein molecules observed in nature, researchers have now engineered ten large, 120-subunit, two-component protein complexes. These designed nanomaterials are attractive starting points for new approaches to targeted drug delivery, vaccine design, and bioenergy. Read more »
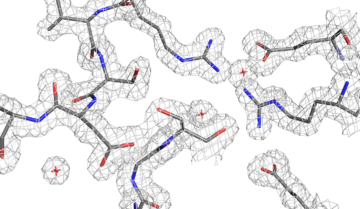
Molecular Switch Triggers Bacterial Pathogenicity
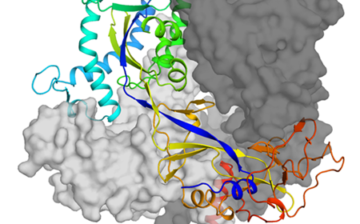
Using an array of high-powered x-ray imaging techniques at the ALS, scientists have revealed for the first time the molecular steps that turn on bacteria’s pathogenic genes. The study could open up new avenues in the development of drugs to prevent or treat bacterial infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
Understanding the Key to Henipavirus Infection
The Hendra virus was the first member of the genus Henipavirus, an emergent group of viruses with a high mortality rate. Knowledge of the protein structure that mediates Hendra entry into host cells could enable the design of antigens with improved immunogenic response. Read more »
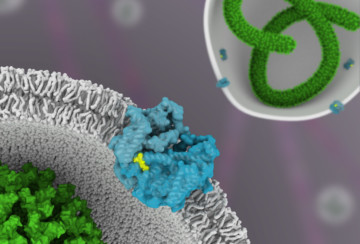
Shutting Out Ebola and Other Viruses
Researchers have used protein crystallography at the ALS to understand how a drug molecule that has shown some efficacy against Ebola in mice inactivates a membrane protein, called TPC1, used by viruses to infect host cells. Read more »![]()
![]()
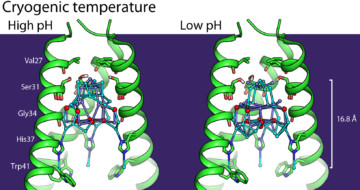
Improving Anti-Influenza Medications
Protein crystallography at ALS Beamline 8.3.1 helped scientists understand the M2 proton-channel structure from the influenza A virus, an understanding that is needed to design better anti-influenza medications. Read more »
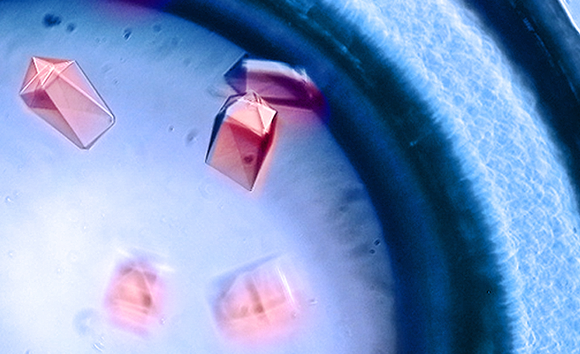
Improving Meningococcal Vaccines
Scientists have found a way to improve the stability of an essential antigenic protein to develop vaccines with higher efficacy for prevention of bacterial meningitis. Read more »
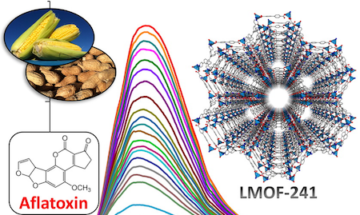
Luminescent MOFs for Mycotoxin Detection
Crystal diffractometry at ALS Beamline 11.3.1 helped scientists develop and understand a new, highly sensitive luminescent metal–organic framework for mycotoxin detection. Read more »
A New Pathway for Radionuclide Uptake
Scientists have reported a major advance in understanding the biological chemistry of radioactive metals, opening up new avenues of research into strategies for remedial action in the event of possible human exposure to nuclear contaminants. Read more »![]()
![]()
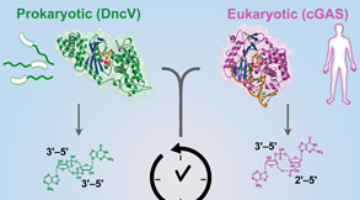
A New Link Between Human and Bacterial Signaling Machinery
Researchers showed that a bacterial signaling protein critical for pathogenesis in Vibrio cholerae is actually a homolog of the human enzyme, cGAS, which detects invading DNA. These results reveal a surprising evolutionary connection between bacterial signaling and human innate immunity. Read more »
Infrared Mapping Helps Optimize Catalytic Reactions
A pathway to more effective and efficient synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other flow-reactor chemical products has been opened by a study in which, for the first time, the catalytic reactivity inside a microreactor was mapped in high resolution from start to finish. Read more »![]()
![]()