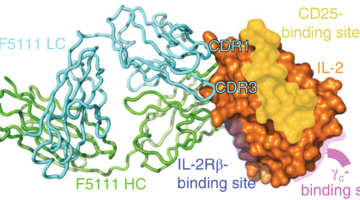
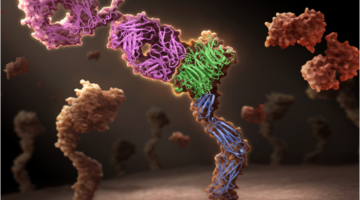
The balance between two types of white blood cells is disrupted in autoimmune diseases. Using protein crystallography, scientists have identified a human antibody that locks interleukin-2, a signaling protein, in a conformation that preferentially activates one cell type to restore the balance and treat autoimmune diseases. Read more »
Modified Antibody Clarifies Tumor-Killing Mechanisms
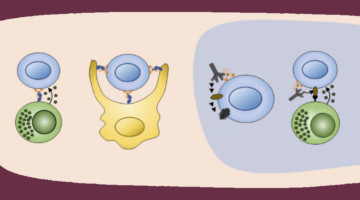
An antibody was modified to activate a specific pathway of the immune system, demonstrating its value in killing tumor cells. The work provides a platform for disentangling different immune-system pathways and could lead to the design of improved immunotherapies. Read more »![]()
![]()
SIBYLS Beamline Builds on Nobel Research
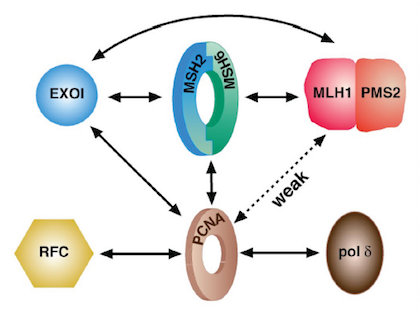
Often the full impact of a scientific discovery takes decades to realize, during which the research is developed further and adopted by other scientists. Such was the case for the work of biochemist Paul Modrich, one of three recipients of this year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source was a core resource Modrich used to build on his earlier work. Read more »
Ancient Proteins Help Unravel a Modern Cancer Drug’s Mechanism
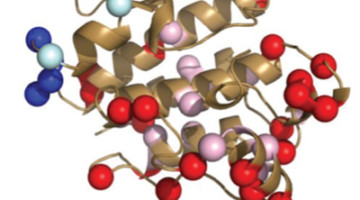
The cancer drug Gleevec is extremely specific, binding and inhibiting only the cancer-causing tyrosine protein kinase Blc-Abl, while not targeting homologous protein kinases found in normal, healthy cells. Researchers at the ALS have uncovered exactly why that is the case, pointing to novel methods of drug discovery. Read more »![]()
![]()
Designer Proteins Target Epstein-Barr-Virus-Associated Cancer
Researchers used new protein design approaches to develop a potential inhibitor of Epstein-Barr-Virus-associated cancer. The study shows not just how to help defeat the virus, but also opens up a whole new way to design proteins against viruses and ultimately, cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
Genentech Uses ALS Crystallography for Therapeutic Antibody Research
Genentech has developed a unique one-armed antibody, onartuzumab, which is now in late-stage clinical trials in multiple cancer types. The company used crystal structures obtained at ALS Beamline 5.0.2 to demonstrate the mechanism of action of this unique potentially therapeutic antibody. Read more »![]()
![]()
Structural Biology Helps Drug Discovery
Last year, drug discovery company Plexxikon made front-page news with its highly successful anti-cancer drug, Zelboraf, a product that was chemically optimized using data from ALS x-rays. Designed to disrupt malignant melanoma, the drug was so successful in human testing that trials were halted so that patients in the trial could all be given Zelboraf. Zelboraf marked a significant advancement for patients with metastatic melanoma who historically have had very limited treatment options.
Read more »![]()