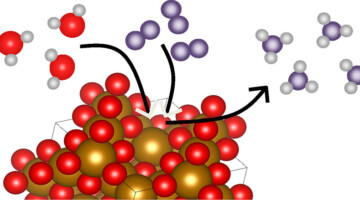
Ammonia is a critical ingredient in many important industrial and agricultural applications. The Haber–Bosch process is the primary process for large-scale ammonia production. A new study uses an experimental–theoretical approach to uncover how interfacial chemistry at the magnetite–water interface drives ammonia synthesis under ambient temperature and pressure. Read more »![]()
![]()
Catalysts Get a Boost with Atomic-Level Tinkering
A research team led by Berkeley Lab designed and fabricated catalysts by precisely tuning the co-localization of active metals—key catalytic centers for specific steps in reaction pathways—offering a new level of control over catalytic performance. Read more »
Catching “Hydrogen Spillover” onto a Catalytic Surface
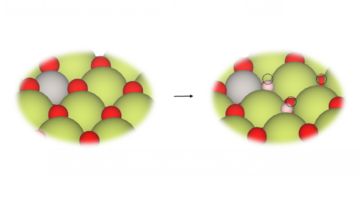
Researchers uncovered the precise mechanism of hydrogen spillover (H2 splitting and migration) onto a catalytic surface by watching it happen under various conditions. The research lays the foundation for designing more efficient catalysts and storage materials essential for next-generation hydrogen energy technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
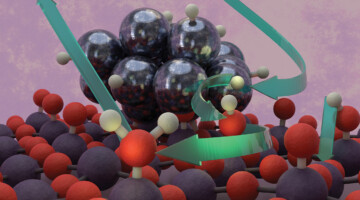
Operando Unveiling of Hydrogen Spillover Mechanisms on Tungsten Oxide Surfaces
An artistic depiction of hydrogen spillover on Pt/WO3, illustrating H2 activation and dissociation on Pt metal clusters, followed by hydrogen migration to WO3 for water formation. At elevated temperatures, water desorption and surface-to-bulk diffusion of hydrogen drive tungsten redox and oxygen vacancy formation on the surface of WO3. Read more »
Excited States in CO2 Clusters Shed Light on Astrochemical Formation Mechanisms
A vacuum ultraviolet photoionization study conducted at the ALS revealed a new mechanism between molecules that converts high-energy ultraviolet light into free electrons. The results provide insights into interactions between CO2 and organic molecules, which are crucial for understanding astrochemical interactions as well as green chemistry and renewable energy development. Read more »
Electronic energy transfer ionization in naphthalene–CO2 clusters reveals excited states of dry ice
The interaction between CO2 and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is of interest in astrochemically relevant ices, the transition to renewable energy, and the development of green chemistry. We investigate the VUV excitation of the naphthalene–CO2 complex and observe excited states of CO2 through a newly identified electronic energy transfer ionization mechanism. Read more »
4f-Orbital Mixing Increases the Magnetic Susceptibility of Cp’3Eu
The ability to harness the 4f-orbital anisotropies and magnetic susceptibilities of lanthanide elements is key to their application in molecular magnetism, including as molecular qubits and single-molecule magnets. Here, 4f orbital mixing and its impact on the magnetic susceptibility of a trivalent Eu organometallic complex was analyzed experimentally. Read more »
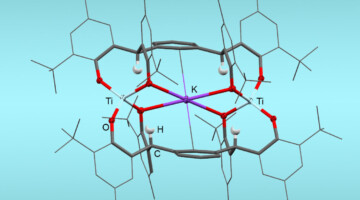
Converting N2 into Usable Form under Ambient Conditions
Researchers learned how molecular structure relates to function in catalysts that convert atmospheric nitrogen into more usable forms at room temperature and pressure. The work could lead to greater energy efficiency in producing nitrogen-based products such as fertilizer where large-scale industrial processes are unfeasible. Read more »![]()
![]()
Kevin Wilson to Receive 2024 Shirley Award
The ALS Users’ Executive Committee will recognize Berkeley Lab Senior Scientist Kevin Wilson as this year’s Shirley Award recipient. At the 2024 User Meeting he will present a talk on using synchrotron radiation to probe the multiphase chemistry of aerosols. Read more »
Caught in the Actinium
In this work, researchers demonstrated a macromolecular scaffold that combines an 8-coordinate synthetic ligand and a mammalian protein to characterize the solution and solid-state behavior of the longest-lived actinium isotope. The information could help design better cancer treatments. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 7
- Next Page »