Researchers identified nitrogen-rich compounds in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered the essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »![]()
![]()
Characterizing Membrane Fouling with Operando Experiments
Membrane filtration offers a cost-effective, energy-efficient approach to purify and desalinate water, but fouling limits the performance of these devices. A new study explored the new experimental design that allows one to study the dynamic fouling process in real time to improve the field’s understanding of how materials deposit, accumulate, and/or crystallize on the membrane’s surface. Read more »![]()
![]()
Dehydration Key Element in Soil Microbe Evolution
A new study illustrates how microbes respond, in real time, to environmental stress, improving the research community’s knowledge of the hidden microbial engines that keep our planet running. Read more »
Bennu’s Ancient Brine Sheds Light on Recipe for Life
Researchers traced the evolution of minerals (“salts”) in an ancient brine, as recorded in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered water and essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »![]()
![]()
Berkeley Lab Helps Explore Mysteries of Asteroid Bennu
The Advanced Light Source and Molecular Foundry provided powerful tools to study asteroid samples returned by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission to the asteroid Bennu. Researchers found a telltale set of salts formed by evaporation that illuminate Bennu’s watery past. Read more »
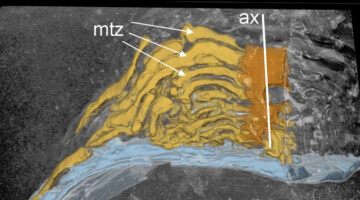
Electron microscopy observations of the diversity of Ryugu organic matter and its relationship to minerals at the micro- to nano-scale
The work reported here addresses the question of how the organic matter (OM) in the Hayabusa2 samples compares and contrasts with OM from primitive carbonaceous chondrites, as observed primarily by transmission electron microscopy in concert with other microanalytical techniques. Read more »
Chemical Insights into the Molecular Composition of Organic Aerosols in the Urban Region of Houston, Texas
This study illustrates the molecular composition of organic aerosols collected in the Houston, Texas, region using direct sampling interfaced with high-resolution mass spectrometry. This study highlights the episodic prevalence and day/nighttime distribution of organosulfates and organonitrates enriched species. Read more »
Pacific Kelp Forests Are Far Older than We Thought
Researchers scanned newly discovered kelp fossils using x-ray tomography at the ALS. The images provided morphological information about the ancient kelp and, along with isotopic analyses, provided insights into the evolutionary history of northeastern Pacific Ocean kelp forests, which flourished more than 32 million years ago. Read more »
Surtsey Volcano: A Rare Window into Earth’s Oceanic Crust
Surtsey, a very young oceanic island in Iceland, emerged through explosive volcanic activity in 1963. Utilizing various techniques, including x-ray microdiffraction at the ALS, researchers gained unique insights into the transformation of volcanic glass to form mineral cements in the basaltic rock of underwater volcanoes. Read more »
Shedding Light on Sea Creatures’ Secrets
Exactly how does coral make its skeleton, a sea urchin grow a spine, or an abalone form the mother-of-pearl in its shell? A new study at the ALS revealed that this process of biomineralization, which sea creatures use to lock carbon away in their bodies, is more complex and diverse than previously thought. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 8
- Next Page »