Electronic structure measurements using x-ray absorption spectroscopy suggest that oxygen vacancies contribute to the metal–insulator transition in ultrathin films of LaNiO3. The results give scientists another “knob” to turn to tune this important transition, which could be useful for making advanced electronic devices. Read more »
A Designed Material Untangles Long-Standing Puzzle
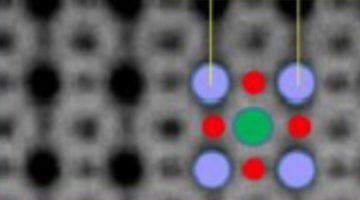
The origin of the metal-to-insulator transition in a key material system was revealed by nanostructures designed to decouple simultaneous phase transitions. This approach could lead to new materials with emergent physics and unique electronic properties, supporting broader research efforts to revolutionize modern electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
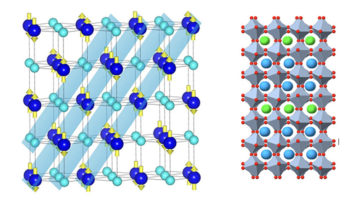
Experimental Evidence of Chiral Ferrimagnetism in Amorphous GdCo Films
Harnessing high‐resolution Lorentz microscopy, Robert Streubel and co‐workers visualize chiral ferrimagnetic domain walls in amorphous films, revealing a composition dependence that potentially enables a temperature control of intrinsic domain wall properties. The reconstructed electron phase (magnetic induction) of achiral Bloch domain walls is shown here. Read more »
A facile route for the synthesis of heterogeneous crystal structures in hierarchical architectures with vacancy-driven defects via the oriented attachment growth mechanism
TiO2 nanorod arrays based on substrates with heterogeneous crystal structures and remarkable crystalline stability have potential as promising photocatalysts. Researchers synthesized a 1D anatase/rutile heterogeneous TiO2 crystal structure in a hierarchical architecture by forming hybrid organic–inorganic interfaces in a solution-based environment. Read more »
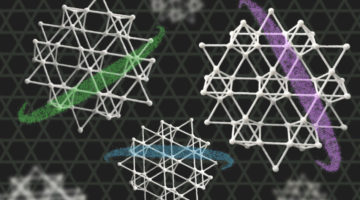
The Electronic Structure of a “Kagome” Material
Scientists have verified exotic electronic properties predicted to emerge in a ferromagnetic material with “kagome” (trihexagonal) lattice symmetry. The greater understanding of kagome materials afforded by this work helps open up a new path toward goals such as ultralow-power electronic devices and quantum computing. Read more »![]()
![]()
From Moon Rocks to Space Dust: Berkeley Lab’s Extraterrestrial Research
Berkeley Lab has a well-storied expertise in exploring samples of extraterrestrial origin. This research—which has helped us to understand the makeup and origins of objects within and beyond our solar system—stems from long-standing core capabilities in structural and chemical analyses and measurement at the microscale and nanoscale. Read more »
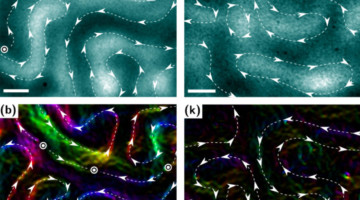
Non-Crystal Clarity: Scientists Find Ordered Magnetic Patterns in Disordered Magnetic Material
Scientists have confirmed the presence chirality, or handedness, in nanometers-thick samples of amorphous (noncrystalline) multilayer materials. The chirality—which potentially could be exploited to transmit and store data in a new way—was observed in the domain walls between neighboring regions of opposite spin. Read more »
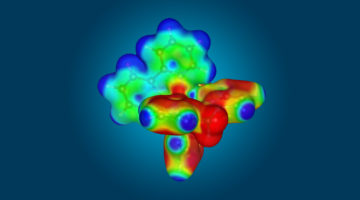
Toward Control of Spin States for Molecular Electronics
Researchers demonstrated, via x-ray absorption spectroscopy, that a molecule’s spin state can be reversibly switched at constant room temperature by magnetism. The results represent a major step toward the goal of programmable, nanoscale molecular electronics for high-speed, low-power, logic and memory applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Imaging Magnetic Microstructure Response to Substrate Strain
A ferromagnetic thin film on a piezoelectric substrate offers a way to control magnetization in ultralow-power devices by relying on coupling between the piezoelectric and ferromagnetic components. At the ALS, researchers were able to image the electrically induced magnetic behavior and correlate it with the piezo-strain driving it. Read more »
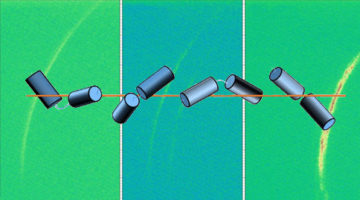
Twisted Structures Emerge from Achiral Molecules
The spontaneous formation of chiral structures from achiral molecules could shed light on the origin of biological homochirality—how one type of chirality dominated the other in certain biological molecules. Here, resonant soft x-ray scattering (RSoXS) has been used to explore helical phases that emerge from achiral asymmetric dimers. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- …
- 26
- Next Page »