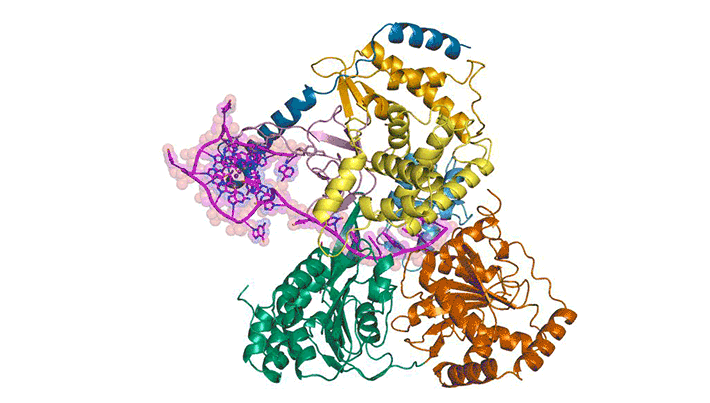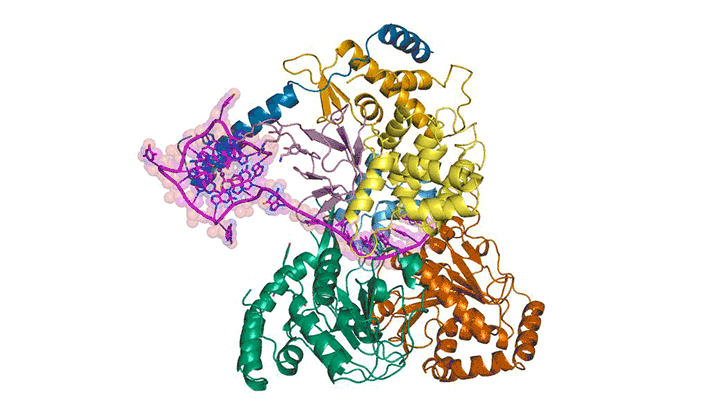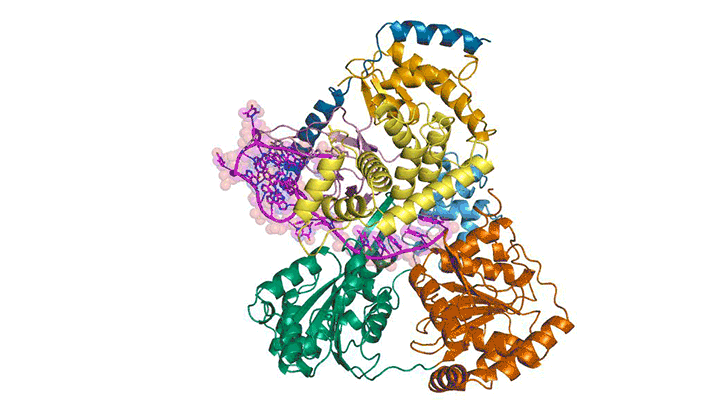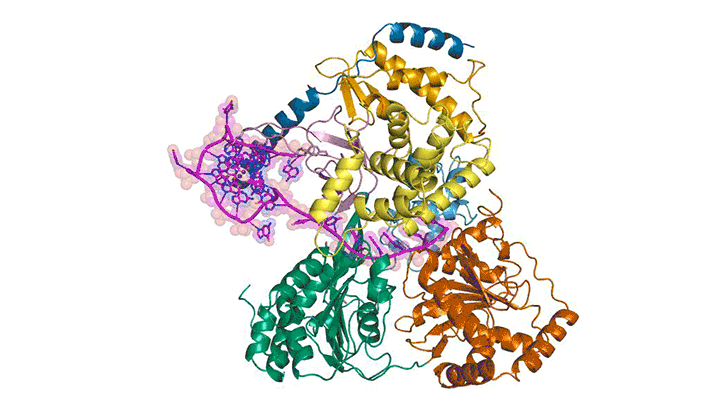
Researchers obtained high-resolution structures of several influenza antiviral drug molecules bound to their proton-channel targets in both open and closed conformations. The structures provide an atomic-level blueprint from which to design more effective anti-influenza drugs that can overcome growing drug resistance. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
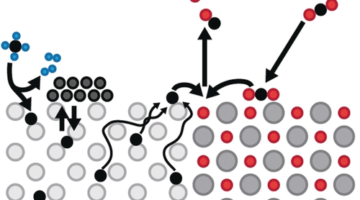
Palladium and Zirconium Convert Greenhouse Gases into Fuel
Greenhouse gases cause the rising global temperatures associated with climate change. At the ALS, researchers have determined that palladium/zirconium catalysts can reduce greenhouse gases like methane and carbon dioxide by converting them into useful fuel. Read more »![]()
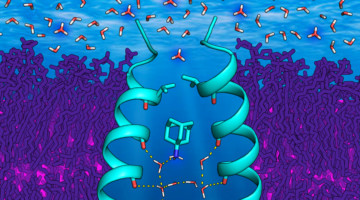
Inhibitors of the M2 Proton Channel Engage and Disrupt Transmembrane Networks of Hydrogen-Bonded Waters
The influenza M2 proton channel can bind to drugs and inhibitors. The ammonium groups of these compounds form hydrogen bonds with networks of ordered waters within the channel, and the adamantyl groups sterically block the diffusion of hydronium into the channel pore. Read more »
Scientists Capture Photosynthesis in Unprecedented Detail
Scientists have captured a more detailed picture than ever of the steps in photosynthesis, the process by which plants use sunlight to split water and produce oxygen while making the carbohydrates that sustain life on Earth. The idea is eventually to have a continuous movie of how water is split into oxygen, and how plants do that using sunlight. Read more »
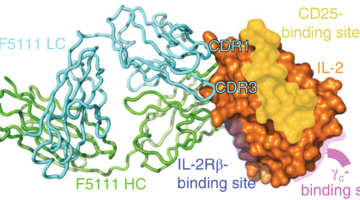
Antibody Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
The balance between two types of white blood cells is disrupted in autoimmune diseases. Using protein crystallography, scientists have identified a human antibody that locks interleukin-2, a signaling protein, in a conformation that preferentially activates one cell type to restore the balance and treat autoimmune diseases. Read more »
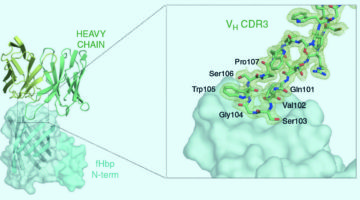
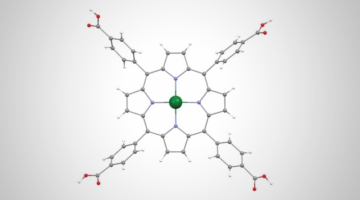
Targeting Bacteria That Cause Meningitis and Sepsis
Researchers determined the structure of a human antibody that broadly protects against a bacterium that causes meningitis and sepsis. The work provides molecular-level information about how the antibody confers broad immunity against a variable target and suggests strategies for further improvement of available vaccines. Read more »![]()
![]()
Unwinding a Quadruple Helix
The double helix is not the only structure formed by DNA and RNA. Guanine-rich DNA and RNA sequences can fold into quadruple-helix structures called G-quadruplexes. Recently, researchers visualized the unfolding of a G-quadruplex by a protein called DHX36, gaining valuable insight into a potential target for drug development. Read more »
A 2D Lattice of Molecular Qubits for Quantum Computing
Researchers developed a way to build a 2D lattice of molecular-spin qubits (quantum bits of information), with control over qubit orientation and localization. The work enables the integration of molecular quantum-information hardware into the scalable, robust, solid-state architectures needed for performing quantum computation. Read more »![]()
![]()
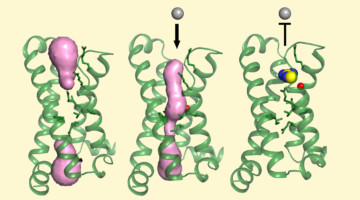
Structure Reveals Mechanism Behind Periodic Paralysis
X-ray crystallography of a membrane protein provided a structural understanding of how a single mutation can result in periodic muscle paralysis. The results suggest possible drug designs that could provide relief to patients with a genetic disorder that causes them to be overcome suddenly with profound muscle weakness. Read more »![]()
![]()
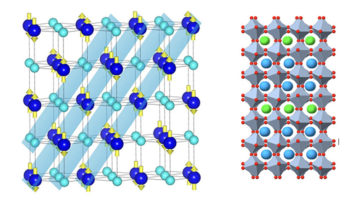
A Designed Material Untangles Long-Standing Puzzle
The origin of the metal-to-insulator transition in a key material system was revealed by nanostructures designed to decouple simultaneous phase transitions. This approach could lead to new materials with emergent physics and unique electronic properties, supporting broader research efforts to revolutionize modern electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- …
- 39
- Next Page »