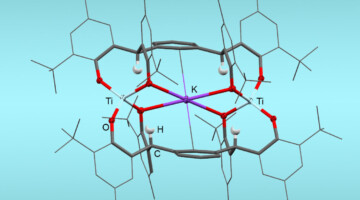
Researchers learned how molecular structure relates to function in catalysts that convert atmospheric nitrogen into more usable forms at room temperature and pressure. The work could lead to greater energy efficiency in producing nitrogen-based products such as fertilizer where large-scale industrial processes are unfeasible. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Cleaner Way to Produce Ammonia
A cavity made from linked rare-earth metals, such as zirconium and titanium, can convert abundant molecular nitrogen (N2) into useful nitrogen compounds, including ammonia or tris(silyl)amines, at room temperature. Read more »
Shaping the Water-Harvesting Behavior of Metal–Organic Frameworks Aided by Fine-Tuned GPT Models
The reticular design and synthesis of metal–organic frameworks enable the structures to be engineered at an atomic level, allowing their properties to be harmoniously harnessed. AI-assisted design of building units can reduce human labor in the enumeration and search for possible structures, thereby accelerating the discovery of MOFs. Read more »
Accelerating Sustainable Semiconductors With ‘Multielement Ink’
Scientists have developed “multielement ink”—the first “high-entropy” semiconductor that can be processed at low temperature or room temperature. The new semiconducting material could accelerate the sustainable production of next-gen microelectronics, photovoltaics, solid state lighting, and display devices. Read more »
Making Renewable, Infinitely Recyclable Plastics Using Bacteria
Scientists engineered microbes to make the ingredients for recyclable plastics—replacing finite, polluting petrochemicals with sustainable alternatives. The new approach shows that renewable, recyclable plastics are not only possible, but also outperform those from petrochemicals. Read more »
Optical sensing of aqueous nitrate anion by a platinum(II) triimine salt based solid state material
Researchers present a new Pt(II) salt that enables the selective and quantitative measurement of aqueous nitrate anions without the need for pH adjustment. The method relies on the color change of the Pt(II) complex from yellow to red and an intense luminescence response, simplifying the detection process for on-site applications and expanding its applicability to broader matrices. Read more »
Valence tautomerism in a cobalt-verdazyl coordination compound
Valence tautomerization in inorganic chemistry typically involves the distribution of electrons between a metal center and redox active ligand, with potential application as molecular switches or other molecular devices. Here we report an example of valence tautomerization and an unusual electronic structure in a cobalt verdazyl complex. Read more »
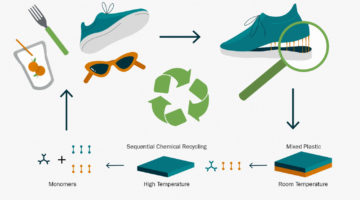
A New Material System for Mixed-Plastic Recycling
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
Ionic Conduction Mechanism and Design of Metal–Organic Framework Based Quasi-Solid-State Electrolytes
This cover image demonstrates the critical role of the solvent in the ion motion of intrinsically anionic metal–organic framework (MOF)–based quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs). Using hybrid theoretical and experimental approaches, we have identified solvent-assisted hopping as the dominant pathway for Li+ conduction in such materials, exemplified by MOF-688. Read more »
A {Ni12}-Wheel-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Coordinative Binding of Sulphur Dioxide and Nitrogen Dioxide
SO2 and NO2 are important air pollutants, and understanding the mechanism of capture materials drives the development of new clean-up technologies. In situ synchrotron x-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic experiments were used to establish a detailed molecular mechanism consisting of reversible coordination of SO2 and NO2 at the six open NiII sites on the unprecedented {Ni12}-wheel of a robust metal–organic framework material at crystallographic resolution. Read more »