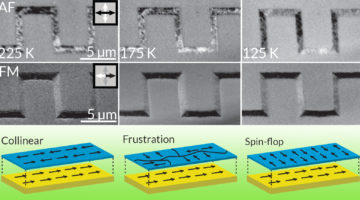
Researchers discovered that the spin configuration of a nanostructured antiferromagnetic material can be affected by the dimensions of features imprinted onto the material. The results suggest that nanoscale patterning can be a viable tool for engineering spin configurations in future antiferromagnetic spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
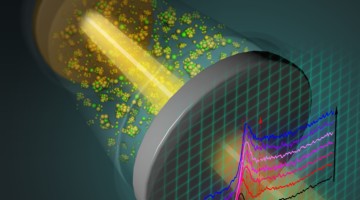
Chemical and Morphological Origins of Improved Ion Conductivity in Perfluoro Ionene Chain Extended Ionomers
Resonant x-ray scattering and x-ray absorption spectroscopy with elemental sensitivity unravel structural features tied to water–ion domains and discern sulfur-containing groups in sulfonated ionomers, which help delineate chemical factors controlling their phase-separated morphology and governing ion transport. Read more »
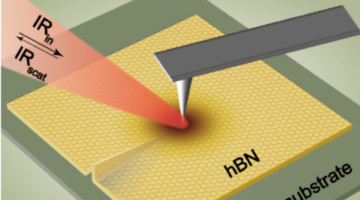
Infrared Nano-Mapping of Local Strain in 2D Materials
Researchers have demonstrated an infrared technique to map and analyze strain in atomically thin crystals of hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) at the nanoscale. This ultrasensitive strain-imaging method could be a promising tool for the examination of low-dimensional materials of interest for electronic and photonic devices. Read more »
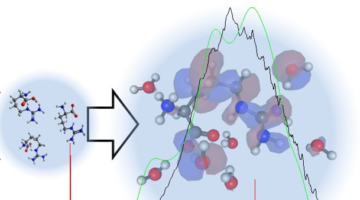
Fundamental Property of Arginine Revealed Through Solvation
Just 20 amino acids act as building blocks for all our proteins, but their chemical properties have been difficult to study at the most fundamental level. Combining experiments and theory at the ALS, researchers have now determined the ionization energy of arginine, an amino acid with over 100 isomers. Read more »
Molecular Framework Imparts Stability to Reactive Catalyst
Researchers have shown that a rigid metal–organic framework (MOF) can be used to stabilize core regions of a reactive catalyst that has potential for use in artificial photosynthesis. The framework immobilizes and preserves key reactive intermediates and affords a clearer view of how the catalyst’s structure correlates with function. Read more »
Catalyst Improves Cycling Life of Magnesium/Sulfur Batteries
Magnesium/sulfur batteries hold promise as a safer, energy-dense advancement, but previous iterations have suffered from extremely limited recharging capabilities. Studies at the ALS provided electrochemical insights into battery polarization and revealed how a titanium catalyst activates magnesium/sulfur compounds to improve battery performance. Read more »
Here Comes the Sun: A New Framework for Artificial Photosynthesis
Scientists have long sought to mimic the process by which plants make their own fuel using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water through artificial photosynthesis devices, but exactly how catalysts work to generate renewable fuel remains a mystery. Now, a study has uncovered new insight into how to better control cobalt oxide, one of the most promising catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
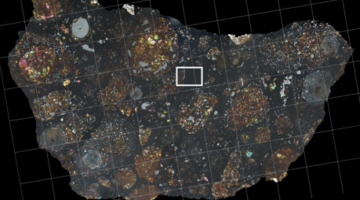
Clues to the Early Solar System Preserved in a Meteorite
Scientists analyzing a tiny carbon-rich pocket inside a meteorite found unexpected chemical signatures. Their findings are the first direct evidence that material from the outer solar system may have traveled inward long before planets formed, providing insight into the early solar system. Read more »
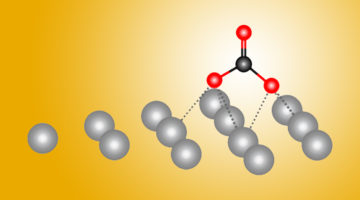
A New Path to Carbon Dioxide Transformation
Combining ALS experiments with quantum-mechanical calculations, scientists found dramatic differences in how carbon dioxide (CO2) reactions begin on silver as opposed to copper. Both metals help transform CO2—a greenhouse gas—into more useful forms, and this new atomic-level data could help make the process more efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
Chiral Crystals Give Rise to Topological Conductors
Researchers have discovered materials whose chiral crystal structures produce chirality in their electronic behavior. These topological conductors retain their unique electronic properties regardless of defects and open new possibilities in materials research. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- …
- 30
- Next Page »