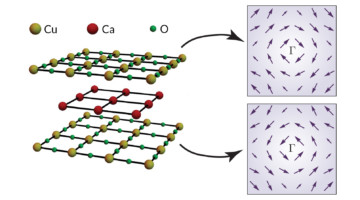
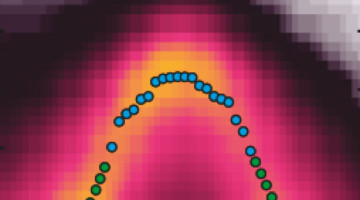
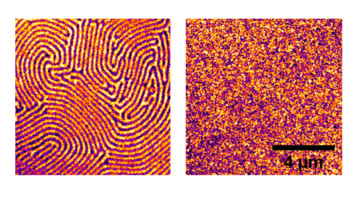
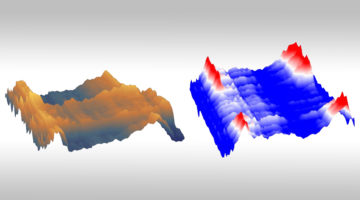
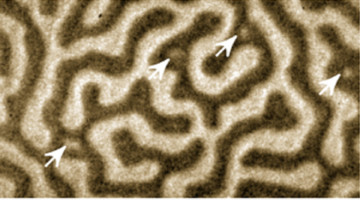
A form of spin-momentum locking, similar to the strong linkage between electron spin and momentum in topological insulators, has been found in a cuprate superconductor. The results open a new chapter in the mystery of high-temperature superconductors, suggesting that new, unexplored interactions and mechanisms might be at play. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Electric-Field Switching of Topological Phase
Researchers have successfully switched a topological insulator on and off by applying an electrical field. The work represents a major advancement toward the creation of a functioning topological transistor that would allow devices to operate more efficiently at lower power than conventional electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Tunable Ferromagnetism in a 2D Material at Room Temperature
Researchers combined soft x-ray spectroscopy and microscopy to demonstrate the tunable ferromagnetic characteristics of a two-dimensional layered material at room temperature. The results open up exciting opportunities for the use of such materials in low-power spintronics, high-density magnetic storage, and flexible electronics. Read more »
Expanding the Infrared Nanospectroscopy Window
An innovative infrared-light probe with nanoscale spatial resolution has been expanded to cover previously inaccessible far-infrared wavelengths. The ability to investigate heterogeneous materials at nanometer scales and far-infrared energies will benefit a wide range of fields, from condensed matter physics to biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
Near-field infrared nanospectroscopy and super-resolution fluorescence microscopy enable complementary nanoscale analyses of lymphocyte nuclei
Recent super-resolution fluorescence microscopy studies have revealed significantly altered nuclear organization between normal lymphocyte nuclei and those of classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Reported here are the first near-field IR imaging of lymphocyte nuclei, and far-field IR imaging results of whole lymphocytes and nuclei from normal human blood. Read more »
Ordered Magnetic Patterns in a Disordered Magnetic Material
Scientists have confirmed the presence of chirality, or handedness, in nanometers-thick samples of amorphous (noncrystalline) multilayer materials. The chirality—which potentially could be exploited to transmit and store data in a new way—was observed in the domain walls between neighboring regions of opposite spin. Read more »
Clues to the Solar System’s Original “Bricks and Mortar”
In comet dust, researchers discovered composite organic-inorganic mineral grains that are likely to be the original “bricks and mortar” of the solar system. “Forensic” samples preserved from the birth of the solar system allow investigations into the nature of the atomic and molecular ancestry of the terrestrial planets and life on Earth. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Manganese Materials Bolster Cathode Capacity
The most expensive component of a battery, the cathode, requires rare transition metals like cobalt. Previous attempts to replace cobalt with inexpensive and non-toxic manganese delivered insufficient performance. Now, researchers have optimized the composition of high-energy-density, high-capacity manganese-based cathodes. Read more »
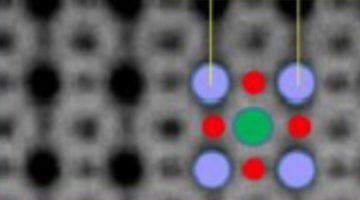
Oxygen Vacancies Matter in the LaNiO3 Metal–Insulator Transition
Electronic structure measurements using x-ray absorption spectroscopy suggest that oxygen vacancies contribute to the metal–insulator transition in ultrathin films of LaNiO3. The results give scientists another “knob” to turn to tune this important transition, which could be useful for making advanced electronic devices. Read more »
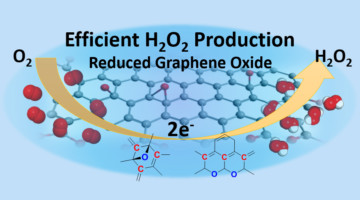
Graphene-Based Catalyst Improves Peroxide Production
Scientists characterized a graphene-based electrocatalyst that potentially makes the production of hydrogen peroxide more selective, efficient, and cost effective. Hydrogen peroxide is an important commodity chemical with growing demand in many areas, including the electronics industry, wastewater treatment, and paper recycling. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- …
- 30
- Next Page »