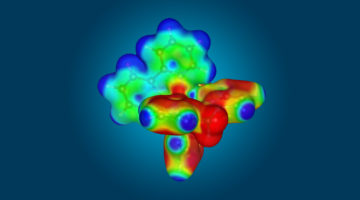
Researchers demonstrated, via x-ray absorption spectroscopy, that a molecule’s spin state can be reversibly switched at constant room temperature by magnetism. The results represent a major step toward the goal of programmable, nanoscale molecular electronics for high-speed, low-power, logic and memory applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Phase Diagram Leads the Way to Tailored Metamaterial Responses
Researchers discovered an innovative way to independently control two optical responses in a single-material system by utilizing the material’s phase diagram. This unique combination of material, methods, and results could lead to a paradigm shift in the design of metamaterial devices that manipulate light. Read more »![]()
![]()
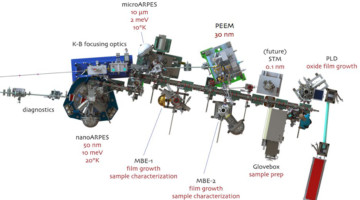
Tuning the Electronic Structure of a 2D Material
The electronic structure of a stacked 2D material was tuned by in situ electron doping, resulting in a large increase in the splitting of two valence bands. Stacked 2D materials possess an array of tunable properties that are expected to be important for future applications in electronics and optics. Read more »![]()
![]()
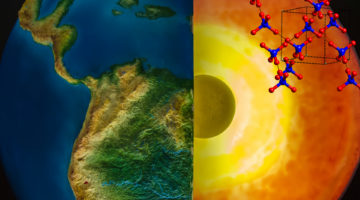
Diamonds From the Deep: Study Suggests Water May Exist in Earth’s Lower Mantle
A new study suggests that water may be more common than expected at extreme depths approaching 400 miles and possibly beyond—within Earth’s lower mantle. The study explored microscopic pockets of a trapped form of crystallized water molecules in a sampling of diamonds from around the world. Read more »
Scientists Confirm Century-Old Speculation on the Chemistry of a High-Performance Battery
Scientists have discovered a novel chemical state of the element manganese. This chemical state, first proposed about 90 years ago, enables a high-performance, low-cost sodium-ion battery that could quickly and efficiently store and distribute energy produced by solar panels and wind turbines across the electrical grid. Read more »
Ingredients for Life Revealed in Meteorites
X-ray absorption spectroscopy and other techniques were used to measure the organic chemical components in a pair of meteorites that crashed to Earth in 1998. The study treads new ground in solar system history and asteroid geology, surfacing exciting possibilities for the existence of life elsewhere in Earth’s neighborhood. Read more »![]()
The Microstructure of a Parrotfish Tooth Contributes to Its Toughness
Parrotfish chew on coral, producing hundreds of pounds of sand each year. Mapping the microstructure of parrotfish teeth, scientists found bundles of crystals interwoven like chain mail. The results provide a blueprint for creating ultra-durable materials for mechanical components that undergo repetitive contact, movement, and abrasion. Read more »
X-Ray Experiments Suggest High Tunability of 2D Material
Using the new MAESTRO platform at the ALS, scientists found that the exotic behavior of electrons in the 2D semiconductor, WS2, may be highly tunable, with possible applications for electronics and other forms of information storage, processing, and transfer. Read more »
Fuel from the Sun: Insight into Electrode Performance
The mechanisms limiting the performance of hematite electrodes—potentially key components in producing fuel from the sun—have been clarified in interface-specific studies under realistic operating conditions, bringing us a step closer to storing solar energy in chemical fuels. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Path to a Game-Changing Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- …
- 30
- Next Page »