Photoemission electron microscopy (PEEM) experiments have demonstrated that the circulation direction of a magnetic vortex can be switched by the application of an electric field, opening the door to digital devices with more streamlined system designs, improved performance, and greater energy efficiency. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
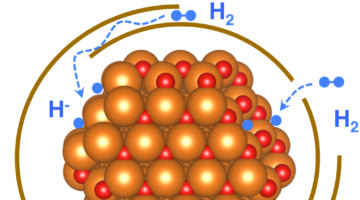
New Study on Graphene-Wrapped Nanocrystals Makes Inroads Toward Next-Gen Fuel Cells
A powdery mix of metal nanocrystals wrapped in single-layer sheets of carbon atoms shows promise for safely storing hydrogen for use with fuel cells for passenger vehicles and other uses. Now, a new study provides insight into the atomic details of the crystals’ ultrathin coating and how it serves as selective shielding while enhancing their performance in hydrogen storage. Read more »
The Mystery of the Lightweight Electrons
Copper oxides are important for superconductivity applications but are difficult to understand due to complex charge, spin, and orbital interactions. Now, studies at the ALS have found such a system in which observations of effective electron mass are at odds with state-of-the-art electronic-structure calculations. Read more »
Amorphous calcium carbonate particles form coral skeletons
Skeletons of Stylophora pistillata corals form by the attachment of amorphous calcium carbonate precursor particles, formed within the coral tissue, to the coral skeleton surface. This mechanism is faster than the precipitation of ions from solution and may render the corals less susceptible to ocean acidification than previously assumed. Read more »
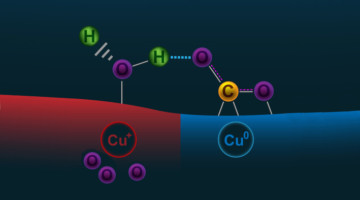
Subsurface Oxygen Boosts Activity of Copper Catalysts
Scientists are seeking ways to reduce levels of CO2 in the atmosphere by improving the processes that convert CO2 gas into ethanol (a liquid fuel). But copper, the best catalyst for this, is not very efficient. Now, ambient-pressure x-ray experiments have revealed how subsurface oxygen boosts copper’s catalytic activity. Read more »![]()
![]()
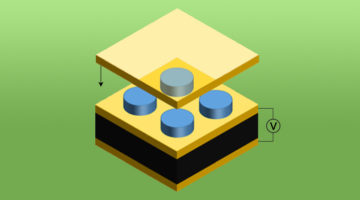
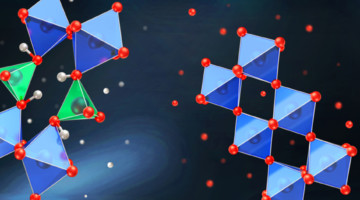
A Multifunctional Material with Electric-Field Control
Three distinct crystalline phases with different electronic, magnetic, and optical properties were reversibly induced in a material through the insertion and extraction of ions by an electric field at room temperature. Such multifunctional materials are desirable for many applications, from smart windows to spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
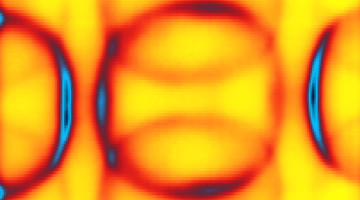
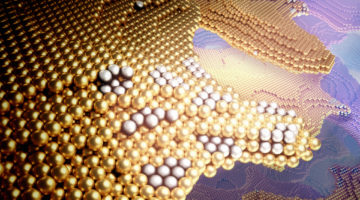
A Closer Look at Dynamic Restructuring in Catalysts
Researchers have structurally and chemically “visualized” the surface of a silver–gold alloy as it reorganizes itself during catalytic activation. The insights gained from this methodology can lead to improved catalysts for energy-intensive industrial applications, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing waste. Read more »![]()
![]()
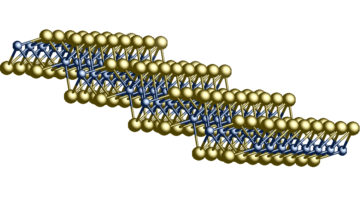
2D Material’s Traits Could Send Electronics R&D Spinning in New Directions
Working at the ALS, researchers have found another family of materials where they can both explore the physics of 2D topological insulators and do experiments that may lead to future applications. The material—known as 1T’-WTe2—bridges two flourishing fields of research: that of so-called 2D materials and topological materials. Read more »
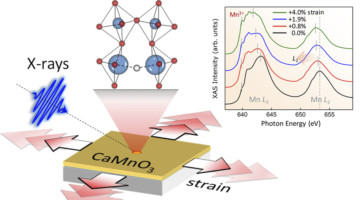
Fine-Tuning Oxygen Vacancies with Coherent Strain
Researchers have demonstrated a novel way to systematically strain-engineer oxygen vacancies in complex transition-metal oxide thin films. The work advances our ability to tailor such defects, small changes in which can lead to dramatic changes in material properties such as conductivity and magnetism. Read more »
A Seaweed Derivative Could Be Just What Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Need
Lithium-sulfur batteries have great potential as a low-cost, high-energy, energy source for both vehicle and grid applications. However, they suffer from significant capacity fading. Now, scientists have found that carrageenan, a seaweed derivative, acts as a stabilizer, allowing for more cycling and an extended lifetime. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- …
- 30
- Next Page »